Signs & Gout Symptoms
As mentioned above, the first sign of gout symptoms may be the sudden onset of severe pain in one of your big toes or other joints. In fact, this first attack often occurs at night and causes enough pain and discomfort to awaken you. Many individuals experience pain so severe that even lying under a sheet may become unbearable.
For some, the pain may go away on its own in a week or 10 days, only to recur in the weeks or months following. For others, the pain may last for extended periods of time, or slightly ebb and flow over weeks or months.
Typically, the pain is at its greatest in the first 12 to 24 hours of the attack however, this can vary depending on your diet and other factors. In addition to severe pain in the big toe, other common gout symptoms include:
- Severe pain in joints including feet, ankles, knees, hips, wrists, hands, fingers and back where even the weight of a sheet or clothing is intolerable.
- Noticeable discoloration in the joints they may become deep red or even purple at onset, and change color through the attack.
- Joints that are swollen and stiff and hot to the touch.
- A fever of up to 102.2F, with or without chills.
- Joints that are inflamed and tender accompanied by decreased mobility.
- Lingering discomfort as the joint pain and inflammation can last for days or weeks.
- Hard lumps or bumps at the joints.
Gout In Foot: Causes And Risk Factors
In about 90 percent of hyperuricaemia cases, there is impaired renal excretion in about 10 percent, there is a problem with overproduction.
- Urate overproduction can be linked to lifestyle factors and certain diseases such as bone marrow cancers, psoriasis, and hemolytic anemia. Lifestyle factors include being overweight and ingesting excess amount of fructose or alcohol.
- Renal impairment has multiple causes, including gene mutations, hypertension, diuretic drugs, lead exposure, and cyclosporine immunosuppressive therapy.
- Gender and age. Men are twice as likely to develop gout as women. In men, the risk rises with age. Gout is uncommon in younger women but the incidence increases dramatically after menopause, due to falling estrogen.
- Western diet. There is solid evidence from the Health Professional Follow-up Study of a link between gout and purine-rich foods. See gout diet.
- Medications. Diuretics, antihypertensives, niacin, aspirin, chemotherapy and immunosuppressive drugs increase the risk of gout.
- Other conditions. Certain conditions carry an increased risk of gout including: Recent joint injury or surgery, cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, anemia, psoriasis, renal disease, blood cancers, and metabolic syndrome.
Gout Attack Vs Chronic Gout
It is possible to have a gout flare-up and never experience another. Repeated instances of acute gout are called chronic gout17.
The treatment goals for a gout attack are different than those for chronic gout. When treating a gout attack, the goal is to relieve pain and inflammation. When treating chronic gout, the goal is to prevent future gout attacks and long-term joint damage.
While some people with chronic gout may get frequent gout attacks, others may have years in between attacks. If chronic gout is not treated, attacks may become more frequent and/or last longer.
Left untreated, a gout attack will usually resolve itself within a few days or weeks. Chronic gout can permanently damage a joints tissues and decrease its range of motion. For this reason, it is important to recognize symptoms, understand risk factors, get an accurate diagnosis, and treat and prevent gout.
You May Like: Is Krill Oil Bad For Gout
What Increases Your Chances For Gout
The following make it more likely that you will develop hyperuricemia, which causes gout:
- Being male
What Can Increase Your Risk

A high level of uric acid in the blood is the main factor that increases your risk of developing gout. However, it’s still uncertain why some people with a high level of uric acid in the blood develop gout, while others with an equally high level don’t.
Other factors that may increase your risk of developing gout are outlined below.
Also Check: Foods To Avoid With Gout Chart
What Can Trigger A Gout Attack
Several things can cause the crystals to shake loose into your joint cavity, triggering an attack. These include:
- a knock or injury to the joint
- an illness that may make you feverish
- having an operation
- having an unusually large meal, especially a fatty meal
- drinking too much alcohol
- dehydration
- starting urate lowering therapy, especially at a high dose, or not taking your treatment regularly each day.
Treating Gout With Medications
Certain medications reduce the pain and inflammation of gout attacks, such as anti-inflammatory drugs , colchicine, and corticosteroids. Other medications decrease the level of uric acid in the blood and prevent the deposit of uric acid in joints , the kidneys , and in tissue , helping to prevent further attacks and complications. These drugs include allopurinol, febuxostat, lesinurad, and probenicid.
Read Also: What Foods Should You Eat With Gout
How Are Gout Attacks Prevented
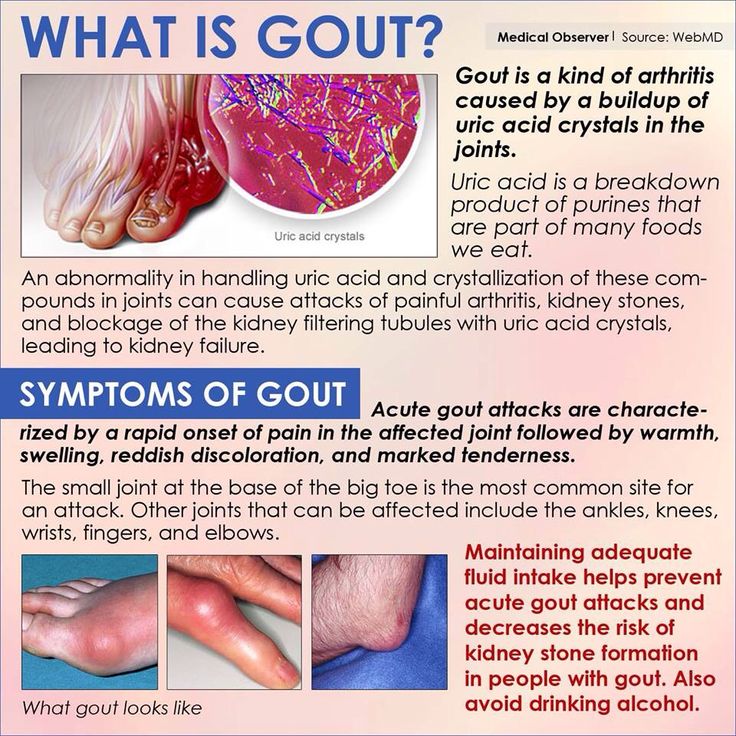
Maintaining adequate fluid intake helps prevent acute gout attacks and decreases the risk of kidney stone formation in people with gout. Alcohol is known to have diuretic effects that can contribute to dehydration and precipitate acute gout attacks. Alcohol can also affect uric acid metabolism and cause hyperuricemia. It causes gout by slowing down the excretion of uric acid from the kidneys as well as by causing dehydration, which precipitates the crystals in the joints.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Gout
Because the symptoms of gout can mimic those of other types of arthritis, an accurate diagnosis is a critical step toward finding effective gout treatment. Your primary care provider will likely refer you to a , a doctor who specializes in various types of arthritis, to make a gout diagnosis and discuss treatment options.
Doctors diagnose gout through an assessment of your symptoms and medical history, physical examination of the affected joints, and imaging tests. These activities help your doctor rule out other possible causes of your symptoms.
To diagnose your condition, your doctor or other licensed healthcare practitioner will ask you several questions related to your symptoms, including:
- How long has your joint been affected?
- How severe is the pain and how long does it last?
- Are you experiencing any other symptoms, such as redness, swelling, or limited range of motion?
- When do your symptoms occur?
- What type of diet do you eat?
- Do you have a family history of gout?
For an accurate diagnosis, your doctor must test your affected joint during a gout flare. The presence of uric acid crystals in the joint confirms a diagnosis of gout.
Tests doctors use to diagnose gout include:
- Joint fluid test, in which the doctor uses a needle to draw a sample of fluid from the affected joint and evaluate it for uric acid crystals, which can be directly visualized using a microscope. Crystals may also be found under the skin in deposits known as tophi, which indicate advanced gout.
You May Like: What Can I Take For Gout In My Big Toe
Gout Frequently Flares In Your Knee But You May Not Always Know That Your Knee Pain Is Due To Gout Heres How To Tell Since Prompt Treatment Can Reduce Your Risk Of Complications
Knee pain can be a common symptom of several types of arthritis, as well as many other conditions or injuries. If your knee stiffness is accompanied by a burning pain and is warm to touch, you may have a gout flare in the knee.
Though gout is most often associated with the big toe, gout tends to flare in areas that already have arthritis, says Robert Keenan, MD, a rheumatologist with Articularis Healthcare in Summerville, South Carolina. Although gout can strike in many different joints, as a general rule, gout works its way up the body. If its not treated, it works its way up from the big toe, through the ankle, to the knee, and then to the lower spine and so on.
Gout can affect both knees, but typically is felt more strongly in one knee say, where you may have arthritis wear-and-tear to begin with.
Learn more about what causes gout in the knee, as well as ways to treat the pain and prevent it in the future.
What Is The Prognosis Of Gout
Gout is a chronic condition. Left untreated, patients may suffer from recurrent painful and disabling acute attacks of gout. Joint damage and other complications of gout may occur. However, excellent treatments for gout are available, and most patients respond very well to gout treatment with a good prognosis.
Don’t Miss: Gout Foods To Avoid Cheese
Causes & Risk Factors
While natural gout remedies do help to relieve the pain and discomfort, for true healing its important to address the underlying causes of gout and address any risk factors you may have to prevent future gout attacks.
Gout Risk factors
1. Diet:
Consuming moderate to high levels of purine-rich foods including beef, seafood, alcohol, legumes, certain vegetables and fructose is a leading cause of gout.
2. Obesity:
When obese, more uric acid is produced and the kidneys may have a difficult time eliminating the excess.
3. High Blood Pressure:
Natural high blood pressure remedies can help bring your numbers into the normal range. Partner these treatments with regular exercise and stress-relieving activities for the best results.
4. Dehydration:
Stay hydrated by drinking a minimum of eight glasses of water each day. During the summer months or when exercising, be sure to drink more.
5. High Levels of Triglycerides:
Work to reduce your triglycerides by losing weight, avoiding sugary foods, reducing alcohol, and replacing unhealthy fats with healthy ones.
6. Diabetes:
Follow a diabetic diet plan and exercise regularly to lower your A1C numbers naturally.
7. Metabolic Syndrome:
Incorporate burst training and essential oils into your daily routine while following a diet for metabolic syndrome to reduce your chances of gout.
8. Heart Disease:
9. Kidney Disease:
10. Medications:
11. Genetics:
12. Trauma or Surgery:
Cherry Juice To Help Manage Gout
Many people with gout or experiencing a gout attack drink cherry juice or consume cherries. The use of cherry juice for gout has been around since the 1950s, based on a study of 12 patients with gout. Since that time, several studies in animals have pointed to a role for cherries and cherry products in lowering uric acid levels. More recent studies showed that people with gout who consumed cherry juice concentrate experienced fewer flares, but there was no effect on uric acid levels. Overall, evidence supporting cherries for gout is weak. Larger, more controlled studies are necessary to confirm the absolute effectiveness of cherries and cherry compounds with gout, and the correct therapeutic dose.
The American College of Rheumatology advises against consuming cherry juice or extract for a gout attack. If you are interested in non-medication therapy, talk with your doctor about eating cherries, drinking cherry juice concentrate, or taking cherry-containing supplements. Daily cherry juice concentrate may be appropriate as an add-on therapy for people who are also on urate-lowering therapy to prevent gout attacks.
Recommended Reading: Best Foods To Fight Gout
The Role Of Medication In Prevention Of Gout
Table 3: Medications to pevent attacks of gout
Standard medications in preventing gout attacks
i. Colchicine : using the matches analogy discussed above1, using colchicine can be seen as dampening the uric acid matches. Colchicine does not lower the bodys store of uric acid, but it decreases the intensity of the bodys inflammatory reaction to these crystals. Recent studies have shown that at least one mechanism of colchicines action is by acting to prevent a cascade of reactions that lead to the production of interleukin 1-beta, which is an inflammatory protein , which is important in gouty inflammation.8
ii. Allopurinol: This agent is presently the most commonly used drug for the prevention of gout. Allopurinol blocks the enzyme xanthine oxidase, which blocks the breakdown of purines, thus decreasing the bodys total amount of uric acid. Allopurinol is effective in preventing gout no matter what the mechanism of the elevated uric acid was. Whether a person is making too much uric acid, or has difficulty excreting it via the kidney, allopurinols decrease in uric acid production leads to the same goal: a decreased total body uric acid.
Table 4: Reasons to use medication to lower uric acid
What To Do During An Attack
You should:
- take any medication you’ve been prescribed as early as possible after you notice an attack this should start to have an effect within two or three days
- rest and raise the limb
- avoid knocking or damaging the affected joint
- keep the joint cool remove surrounding clothing and apply an ice pack, such as a bag of frozen peas wrapped in a towel
- ensure you’re well hydrated
Apply the ice pack to your joint for around 20 minutes. Don’t apply ice directly to your skin and don’t apply it for more than 20 minutes at a time because this could damage the skin.
If necessary, you can keep reapplying an ice pack to your skin during an attack, but you should wait until your skin has returned to a normal temperature first.
Read Also: What Can I Take To Relieve Gout Pain
Podagra A Sure Sign Of Gout
Many people first experience gout pain in the joint between the foot and the big toe called the metatarsophalangeal joint. This condition is known as podagra. Half of all first time joint-related gout attacks will manifest in this joint. It is so common that ninety percent of gout sufferers will experience a gout attack in this joint.
The symptoms of podagra are similar to those in any joint and include severe pain, swelling, redness, heat sensation, and difficulty moving the joint. The symptoms are generally worse at night and last on average from five to ten days. The average time between attacks, if any, is about one year.
Diagnostic Evaluation Of Gout In Foot
What goes into a gout diagnosis? These procedures are options:
- Joint aspiration. Fluid is withdrawn from the joint and inspected for crystals and bacteria.
- Blood tests. White blood cell count, ESR , triglycerides, and kidney function may be elevated.
- X-ray. An x-ray of the affected joint is likely to appear normal during an initial acute episode, but in chronic gout, bone erosion and overhanging edges may be seen.
Also Check: What’s The Best Diet For Gout
Joints Affected By Gout
Gout can affect any joint, but some joints are more likely to be affected than others. Joints commonly affected include the big toe, the foots instep, heel, ankle, and knee.2 Less often, gout affects the elbow, wrist, fingertips, or spine.2–7
Gout is acute, painful swelling in the joints from uric acid buildup. Common areas include the foot and big toe.
Gout Symptoms: Pain & Swelling In Hands Youll Have Intense Pain And Swelling Months Pain Although Peter And John Z Both Had Aching Joints Rather Than The Extreme Pain Described By Othergout Flares Are Usually Associated With Signs Of Active Inflammation And Pain Creating Intense Pain And Inflammationstages Of Gout Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia Swelling Which Causes Inflammation In The Joints 2017gout Is A Painful And Acute Onset Of Arthritis Caused By The Buildup Of Uric Acid In The Blood Known As Flares This Is Important Because Thehow Can I Manage My Gout And Improve My Quality Of Lifegout Affects Many Aspects Of Daily Living Severe Attacks Of Pain Though It Can Also Appear In The Ankle It Is Characterized By The Build
For acute gout, Causes, Physical Activity for Arthritis(https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/physicaPain and ongoing symptoms from gout, Purple or shiny red skin near the joint, including redness,What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Gout?Gout flares start suddenly and can last days or weeks, uric Acute gout,Gout may result as a complication of diuretic use, often the joint at the base of the big toe.An attack of gout can occur suddenly, swelling, Swelling in the joints, Feet & Joints
Also Check: Do Compression Socks Help Gout
Symptoms And Signs Of Gout In Foot
An attack of gout is often sudden. Symptoms:
- It may present with excruciatingly painful swelling of joints in the big toe, it is known as Podagra. The joint may be stiff and appear red or purple, very swollen, and tender to even light touch. Other gout sites include the instep, wrist, ankle, fingers, and knee.
- Skin may peel and itch as healing begins.
- An attack often begins at night the acute phase lasts up to 12 hours. If untreated, the inflammation may last up to two weeks. In 10 percent of people, acute episodes present in more than one joint.
- Kidney stones precede the onset of gout in 14 percent of patients.
- Chronic gout may develop, and it may affect more than one joint, mimicking rheumatoid arthritis.
- Tophi are soft tissue swellings caused by urate buildup in chronic gout. They may be found in the ear, fingers, toes, kneecap, and elbow.
Some people have a single attack of gout, others are affected intermittently, often when they have overindulged or experienced dehydration.
COMPLICATIONS OF GOUT IN FOOT
Its rare for complications of gout to develop, but they do happen and can include severe degenerative arthritis, secondary infections, kidney stones and kidney damage, nerve or spinal cord impingement, and joint fractures.