Common Diseases That Overlap With Lupus
Although lupus usually occurs alone, people with lupus may experience symptoms typical of one or more other connective tissue diseases. In these cases, a physician may use the term overlap to describe the illness.
Common diseases that overlap with lupus:
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
There are also many less common autoimmune diseases that can affect people with lupus.
Who Is Affected By Cppd
CPPD affects both men and women. It occurs more frequently in people as they age, commonly affecting people over age 60.
People who have an increased risk for CPPD include those with:
- A thyroid condition.
- · Low magnesium.
- · Disorders that affect calcium, phosphate or iron metabolism .
The condition is also commonly present in people who have osteoarthritis/degenerative joint disease. “Attacks” of osteoarthritis associated with pain, swelling and redness of the joint may in fact, in certain cases, be due to CPPD.
CPPD in young patients is unusual. Its occurrence should lead the doctor to look for certain metabolic and hereditary disorders.
Overlapping Diseases Are Most Likely To Develop Shortly After The First Diagnosis
There is no time limit on when a second overlapping autoimmune disease may develop, although it is most likely to happen shortly after the first diagnosis.
Nevertheless, it is still possible to develop a second autoimmune disease more than ten years after the diagnosis of the first.
It is important to keep the lines of communication open with your healthcare provider to discuss all of the symptoms you are experiencing and ensure any potential overlapping diseases are recognized.
Don’t Miss: Almond And Gout
How Is Pseudogout Diagnosed
Your doctor may draw fluid from your joint to check for the crystals that cause pseudogout. X-rays might also show some buildup of crystals or signs of joint damage. Your doctor will probably want to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms, such as gout, osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Can Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Be Prevented
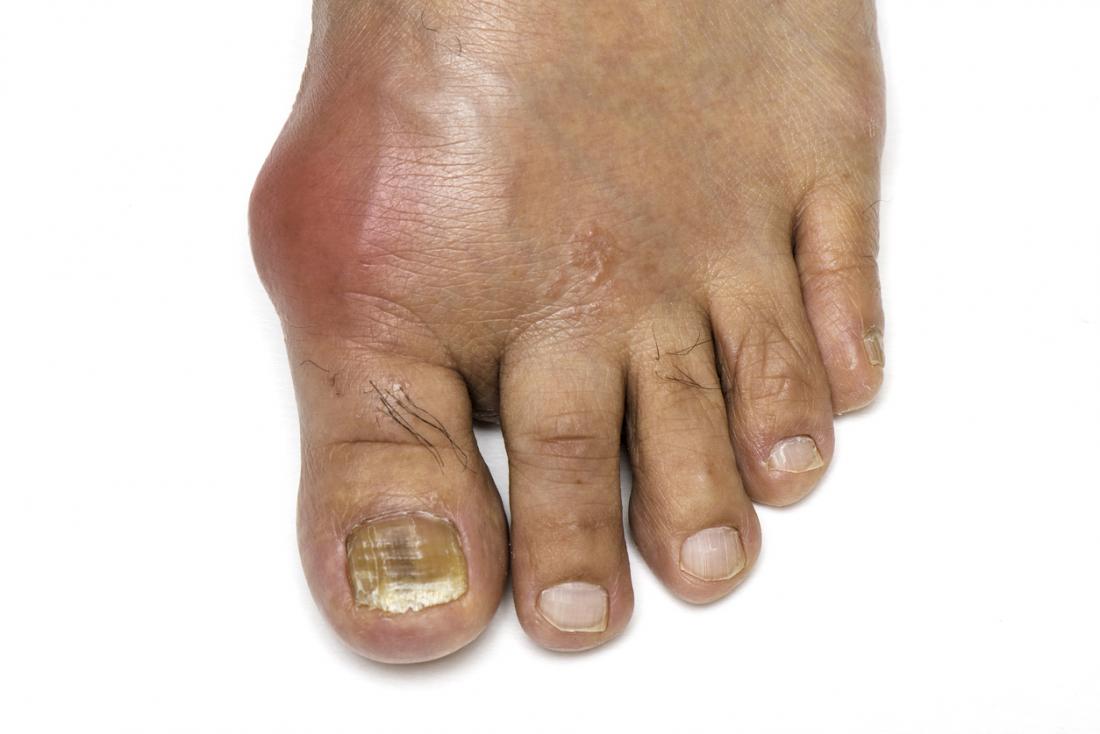
Unlike gout, there is no treatment or diet that can prevent the formation of CPP crystals. If an underlying condition caused an episode of pseudogout or low magnesium levels), treating this may prevent further attacks.
Like osteoarthritis, the damage from chronic CPP crystal arthritis can be limited by keeping your weight normal and getting a moderate amount of exercise.
You May Like: Is Pistachio Bad For Gout
Age Raises The Risk Of Pseudogout
Anyone can develop pseudogout, but the risk increases significantly with age. The crystal deposits associated with pseudogout affect about 3 percent of people in their 60s. The percentage increases to about 50 percent of people in their 90s. The condition is equally prevalent among women and men.
The risk of developing the condition is also increased if the patient has any of the following metabolic disorders:
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Ochronosis
- High iron levels
- Hypercalcemia
What Happens To Patients With Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease
Prevalence of chondrocalcinosis varies from 7-10% in people aged 60 years, and shows equal sex distribution. Chondrocalcinosis is strongly associated with age the prevalence is low below 50 years old, and increasing from 10%-15% in those aged 65-75, and 30%-60% in those older than 85. Chondrocalcinosis is reported from most countries and racial groups.
Genetic associations include mutations of the ANKH gene on chromosome 5p and unknown genes on chromosome 8 . The ANKH gene functions to transport inorganic pyrophosphate out of the cells. Familial mutations result in a gain of function of the ANKH that increases extracellular PPi and leads to onset of CPPD disease in the third or fourth decade of life.
There have been numerous associations suggested with metabolic diseases, but many reflect chance concurrence of common age-related conditions. The strongest evidence for association is with hyperparathyroidism, hemochromatosis, and hypomagnesemia and hypophosphatasia .
There is strong overlap with OA, however its relationship is complex, but with convincing evidence for a strong positive association, at least in the knee.
Occasional development of rapidly progressive arthropathy is well recognized, particularly at the knee, shoulder, or hip. This destructive pyrophosphate arthropathy is mainly confined to elderly women, associated with a poor outcome.
You May Like: Is Pickle Juice Good For Gout
What Is Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease is a form of arthritis that causes pain, stiffness, tenderness, redness, warmth and swelling in some joints. It usually affects one joint at a time, but sometimes it may affect several joints at once.
The symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other diseases, especially gout . Some symptoms of CPPD may appear to be symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
CPPD commonly affects the knee or wrist. Less often, it can involve the hips, shoulders, elbows, knuckles, toes or ankles. Rarely it affects the neck and causes neck, shoulder pains, headaches and in some cases fevers. This occurs when the calcium crystals deposit around the dens part of the second cervical vertebra. The condition is called crowned dens syndrome.
How Is Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease Treated
The treatment of CPPD is similar to the treatment of acute gout attacks with anti-inflammatory medication. Uric acid-lowering drugs are not prescribed. Symptoms are often relieved within 24 hours after beginning treatment with anti-inflammatory medications.
The goals of treatment are to relieve pain and inflammation, and prevent recurrent attacks that could lead to significant pain and joint damage.
The type of treatment prescribed will depend on several factors, including the person’s age, type of other medicines they’re taking, overall health, medical history and the severity of the attack.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs are usually continued until the CPPD attack completely resolves. If side effects from the therapy occur, treatment may be changed to a different medicine. Your healthcare provider will discuss the potential side effects with you.
Side effects of medicines
Not all patients will develop side effects from these medicines. How often any side effect occurs varies from patient to patient. The occurrence of side effects depends on the dose, type of medicine, length of treatment, concurrent illnesses and other medications the patient may be taking.
Some side effects are more serious than others. Before any medicine is prescribed, your healthcare provider will discuss with you the potential benefits and risks of taking the medications.
Read Also: Are Almonds High In Purines
Risk Factors For Pseudogout
The following risk factors are associated with higher rates of pseudogout, which may be called CPPD disease or acute CPP crystal inflammatory arthritis. Unlike gout, pseudogout is not influenced by diet,1 sex, or ethnicity.2
Most of these risk factors, such as age and genetics, cannot be changed. Underlying conditions that increase risk may be addressed with treatment.
What Are Pseudogout Symptoms And Signs
Pseudogout can result in arthritis of a number of joints. The most common joint affected is the knee, but it can also involve the wrists, shoulders, hips, and/or ankles. Pseudogout usually affects only one or a few joints at a time. The “attacks” of joint inflammation, characterized by acute joint swelling, warmth, stiffness, and pain, may last for days to weeks and can resolve spontaneously. The inflammation leads to loss of range of motion and function of the involved joint.
You May Like: Are Oranges Good For Gout
What Are Causes Of Pseudogout
Pseudogout is primarily caused by the precipitation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals developing within a joint space. Pseudogout has sometimes been referred to as calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease or CPPD.
Pseudogout is clearly related to aging as it is more common in the elderly and is associated with degenerative arthritis. Acute attacks of the arthritis of pseudogout can be caused by dehydration. This is particularly common in hospitalized patients and those recovering from operations, especially when associated with dehydration. Pseudogout can also be caused by the hormonal effects on calcium metabolism from hyperparathyroidism.
How To Prevent Arthritis And Other Joint Pains
To date, there is no cure for arthritis. However, getting the right treatment approach coupled with eating the right food can help control the symptoms of arthritis from worsening.
There are a lot of medical approaches in alleviating the pain and discomfort caused by arthritis. The best approach for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis is interventional pain management.
Also Check: Is Onion Bad For Gout
Common Diseases Treated By A Rheumatologist
IBJI
July 17, 2012 | Blog
As we have discussed in the past, a rheumatologist can treat a wide variety of diseases and conditions. Many people know that arthritis , lupus, and fibromyalgia are best treated by a rheumatologist. What most people dont know is that these diseases fall into a confusing category called autoimmune diseases. To help clear up the confusion here are some of the more common diseases that rheumatologist treat:
What Is Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals can become deposited on cartilage and various other tissues in and around joints. This is known as CPP deposition . Some people have CPPD on the cartilages that cover their joints. This is known as chondrocalcinosis. It may cause no symptoms but may be picked up on an X-ray. Other people may have an attack of joint pain and swelling identical to gout. This is called pseudogout, or acute CPP crystal arthritis. There is also a longer-term condition called chronic CPP crystal inflammatory arthritis. Some people with osteoarthritis get CPPD and, when this causes symptoms, it is referred to as osteoarthritis with CPPD.
Also Check: Almond Milk And Gout
Symptoms Can Be Controlled But Not Cured
There is no cure for pseudogout, but medications can treat the symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory are usually prescribed to control pain and inflammation during pseudogout attacks. For the purpose of preventing further attacks, low doses of Colcrys and NSAIDs are typically prescribed, along with recommendations for proper hydration. Cortisone shots into the affected joint may be another option for controlling pain and inflammation, especially for people who cannot use the other medications. Surgery is also an option for severely damaged joints.
The Joint Fluid Test Is The Gold Standard
The most significant diagnostic test for determining pseudogout is a joint fluid examination. Joint fluid is drawn from the affected joint and examined for rod-shaped or rhomboid-shaped CPP crystals .
Based on the observation of these crystals, the diagnosis can be confirmed. X-ray evidence also supports the diagnosis when chondrocalcinosis is detected. If needed, more lab tests can be performed to rule out other types of arthritis.
Also Check: Is Almond Milk Good For Gout
Does Colchicine Work For Pseudogout
Colchicine, often used in the treatment of gout, is also sometimes helpful in pseudogout management. In pseudogout, colchicine has been found to reduce inflammation and slow the production of CPP crystals. It can therefore be used as a treatment for an acute attack of pseudogout and as a preventative treatment in people who have frequent attacks.
What Are The Causes Of Arthritis
Arthritis results from a variety of factors depending on the type of arthritis. Here are the common causes of each type of arthritis:
Aside from these condition-specific causes, other common causes for arthritis are obesity and family history.
Recommended Reading: Gout And Tofu
Factors That Reduce Risk
Alcohol and tobacco abuse disorders, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, diabetes, and hypertension seem to lower the risk of developing CPPD disease, including pseudogout.4 While these conditions are associated with a lower risk of pseudogout and other forms of CPPD disease, their negative effects on health and well-being are significant and therefore not desirable.
Similarly, certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, and loop diuretics have been associated with a lower risk of CPPD disease, including pseudogout.4 However, these medications carry potential side effects and are not recommended for lowering the risk of CPPD disease.
Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disorder
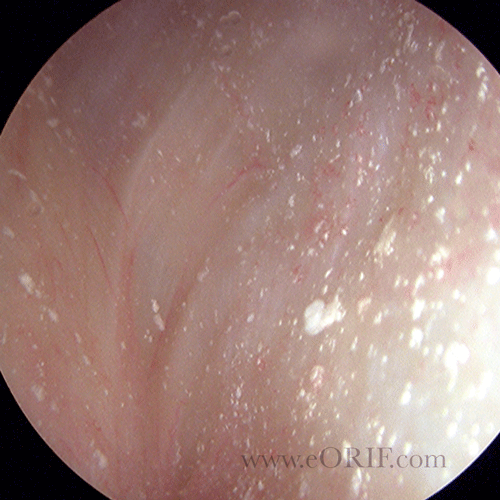
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disorder is a chronic type of arthritis that causes joint problems due to an accumulation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in and around the joints and tendons. It most commonly affects the knees, wrists, and hips.
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition can cause calcification of the tendons and ligaments which can be severe and debilitating. This typically affects the tendons around the shoulder joints and the Achilles tendon but any joint can be affected.
The disease is sometimes presents similar to gout because both diseases are caused by a build-up of crystals in the joints that trigger a response by the immune system.
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition typically affects men and women over the age of 50. It is often found in and around joints typically affected by osteoarthritis, especially the knees.
You May Like: Almond Good For Gout
How Should Patients With Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease Be Managed
There is no current treatment for CPPD deposition disease. Unlike in gout, there is no practical way to remove or dissolve CPP crystals from the joints articular cartilage or soft tissues. No treatment can modify the progression of structural changes.
Treatment of associated metabolic diseases does not result in resorption of CPP crystal deposits and does not influence the outcome of CPPD deposition disease, except possibly for the correction of hypomagnesemia.
General principles
All patients should receive: education about their arthritis, prescription for local strengthening and aerobic exercise, advice on reduction of adverse mechanical factors , and simple analgesia.
Goals of treatment include control of symptoms, early mobilization to avert effects of prolonged immobility, and maintenance or improvement of function. Local therapy is preferred over systemic therapy, if possible.
The treatment of acute attacks of CPP crystal arthritis are predominantly expert opinion-based and modeled on the treatment of acute gout.
Treatment
Non-pharmacologic treatment with ice and temporary rest are beneficial adjuncts to pharmacologic modalities, which should be tailored to individual patients and their comorbidities.
Aspiration alone may be the only treatment needed, which greatly improves symptoms in majority of cases. However, fluid re-accumulation is common.
Simple analgesics or NSAIDs are beneficial.
Systemic corticosteroids are considered for severe, polyarticular attacks.
What Causes Pseudogout
Pseudogout occurs when calcium pyrophosphate crystals form in the synovial fluid in the joints. Crystals can also deposit in the cartilage, where they can cause damage. Buildup of crystal in the joint fluid results in swollen joints and acute pain.
Researchers dont fully understand why the crystals form. The chance of them forming likely increases with age. Crystals form in about half of people over the age of 85, according to the Arthritis Foundation. However, many of them dont have pseudogout.
Pseudogout can often run in families, so many medical professionals believe it to be a genetic condition. Other contributing factors may include:
- hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid
- hyperparathyroidism, or an overactive parathyroid gland
You May Like: Cherry Juice For Gout Mayo Clinic
How Can I Prevent Gout
If gout runs in your family, men in particular should limit alcohol, fats, and foods that are more likely to increase uric acid level in the body. Those include meat, sardines, bacon, mussels, and yeast. Beer, especially, can also bring on a gout attack. Drinking plenty of liquids may help minimize the risk of kidney stones. Your doctor can do blood and urine tests to figure out your potential risk of a gout attack. Itâs also a good idea for men who are at greater risk to keep an eye on their weight.
Medications can also help prevent gout attacks if you have them often. These drugs decrease the production of uric acid or increase the amount of uric acid you get rid of in urine. These medicines include allopurinol , colchicine , pegloticase , probenecid , and rasburicase .
If these medications arenât effective, your doctor may prescribe . If you have heart issues, be very cautious taking febuxostat.
What Are The Symptoms Of Arthritis
The signs and symptoms of arthritis are evident on the joints and surrounding areas. Just like the causes of arthritis, the symptoms depend on the type of arthritis. These symptoms include pain and discomfort, swelling and stiffness, redness, and decreased range in motion.
Other signs and symptoms may also be observed such as warmth on the swollen area, tenderness of the inflamed joint, and loss of grip and strength. Some individuals may also feel restlessness and weakness, fatigue and loss of appetite.
Read Also: Are Almonds Good For Gout
Exercise Programs For Seniors
As people age, their bones, muscles and underlying tissue weaken, resulting in decreased strength, energy, and impaired mobility. Inactivity may increase these effects of aging. Exercise and physical activity can be beneficial to older adults and can help to increase strength, improve balance and possibly delay or prevent diseases such as diabetes, arthritis, osteoporosis and heart disease. …
Is Pseudogout Painful
Acute CPP crystal arthritis, or pseudogout, may cause exactly the same symptoms as gout. Thus, there will be pain, warmth, redness and swelling of one or more joints. Any joint can be involved but the knees are most commonly affected, followed by the wrists, shoulders, ankles, hands and feet.
Chronic CPP crystal arthritis resembles osteoarthritis. It causes longer-term damage to joints, with pain and stiffness. Knees, hips, shoulders and wrists are most often affected.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Allopurinol And Alcohol
What Tests To Perform
Diagnosis of CPPD deposition disease relies on the identification of CPP crystals in the synovial fluid from affected joints by compensated polarized light microscopy in the synovial fluid of affected joints , or on histologic examination of cartilage or synovial biopsies. This is complemented by typical chondrocalcinosis on radiographic findings.
Synovial fluid analysis should always be performed to confirm the diagnosis and to exclude other conditions, particularly septic arthritis or gout. Synovial fluid evaluation should always include cell count, crystals evaluation under compensated polarized microscopy, gram stain and culture. Aspirated fluid in acute CPP crystal arthritis is often turbid with diminished viscosity. Synovial fluid cell count is usually greatly elevated with > 90% neutrophils.
In chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy, synovial fluid findings are more variable, and range from inflammatory to non-inflammatory. CPP crystals are identified under compensated polarized light microscopy as rhomboids or rods with weak positive birefringence .
Crystals of CPP are more difficult to discern and often less numerous than monosodium urate crystals, thus can be missed frequently.
Acute CPP crystal arthritis triggers an acute phase response with often impressive elevation of ESR, C-reactive protein, and peripheral white blood cell count. In chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy, mild anemia and modest elevations of acute phase reactants can occur.
Imaging
Figure 2.
Figure 3.