What Are The Acr Treatment Guidelines For Gout In Patients With Renal Disease
In patients with gout who have moderate to severe kidney disease, ACR guidelines recommend xanthine oxidase inhibitor therapy with either allopurinol or febuxostat as the first-line pharmacologic approach. Probenecid can be used in patients who have contraindications to or are intolerant of at least 1 of those first-line agents, or it may be combined with a xanthine oxidase inhibitor if the inhibitor does not lower uric acid sufficiently. Probenecid could also be used for those patients who consider the risks of xanthine oxidase inhibitors to be too high.
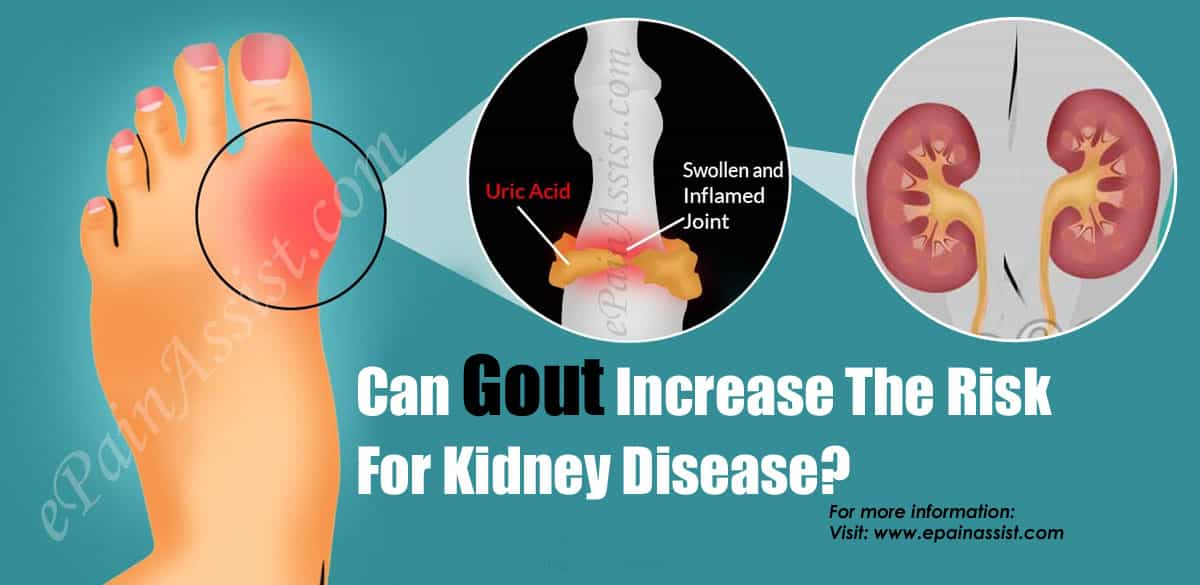
Gout And Kidney Disease
Most commonly, kidney disease can cause gout. However, gout may also lead to kidney disease. Since uric acid is filtered through the kidneys, the two diseases are related. 1 out of 10 people with chronic kidney disease have gout, and an even higher percentage of people with gout have kidney disease. Many people with kidney disease have uncontrolled gout which can make kidney disease worse, and lead to other complications.
Independent Variable/outcome Of Interest
The outcome of interest was incident chronic kidney disease /kidney failure , identified by the occurrence of two diagnoses for CKD at least 4-weeks apart in Medicare claims, identified with International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, common modification codes, 582.xx, 583.xx, 585.xx, 586.xx or 588.xx, with an absence of any CKD code in the baseline 365-day period. This ICD-9-CM code based approach has been used to assess renal disease in the validated Charlson-Romano comorbidity index , and is being currently used by the U.S. Renal Data System Coordinating Center a similar set of codes is also used in Deyo-Charlson index , another adaptation of the Charlson index. This approach is valid with high specificity of 99% and moderate sensitivity of 7088% and a median positive predictive value of 78% . These ICD-9 codes include all CKD stages of the National Kidney Foundation classification of CKD.
Read Also: Gout And Tofu
Hyperuricemia Associated With Nonalcoholic Liver Disease Or Type 2 Diabetes
Experimental studies suggest that intake of added sugars containing fructose have a major role in driving both nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes, and in both conditions, there is evidence that elevations in intracellular uric acid have a contributory role . Hyperuricemia is also a predictor for CKD in subjects with type 2 diabetes . Likewise, the prevalence of CKD is higher in NAFLD patients, and a relationship between the severity of NAFLD and the presence of decreased eGFR or proteinuria has been reported . Moreover, incident CKD is also common in patients having NAFLD diagnosed by ultrasound at baseline . Xanthine oxidase is shed into the circulation mainly from liver cells, and its serum activity is increased in NAFLD patients . These observations raise the possibility that hyperuricemia subjects with type 2 diabetes or NAFLD may benefit from XO inhibitors to prevent or slow CKD progression.
Genes Responsible For Uric Acid Regulation
SLC22A12 gene encodes for the transporter URAT1 present on the apical membrane of renal tubules. SLC2A9 is another gene involved in regulation of UA excretion. It encodes for a transporter protein in the membrane of renal tubules. Polymorphism of both genes results in decreased fractional excretion of UA leading to increased SUA levels. ABCG2 is a gene transporter for UA in the proximal tubular cells of the kidney as well as in the GIT. SLC17A1, SLC17A3 genes are important determinants of SUA levels acting as membrane transporters in the kidenys. Other genes involved in determination of SUA levels include SLC22A11, the glucokinase regulatory protein , Carmil , and near PDZ domain containing 1 genes , .
Also Check: Is Almond Milk Good For Gout
Other Ways To Treat Gout
Medicine is considered the most effective treatment method for gout, but there are lifestyle changes you can make to manage your symptoms during a gout attack, or help prevent gout attacks from happening. Learn more about other ways to manage symptoms of gout during an attack here. Learn more about preventing future gout attacks here.
Educational content made possible by Horizon Therapeutics.
Pathogenesis Of Chronic Gout
Chronicity is a feature of gout. It results from chronic inflammation that follows recurrent attacks of gout. Chronic gout manifests by chronic synovitis, bony erosions, cartilage damage and tophi formation. This can be explained by different mechanisms. Presence of urate crystals in the synovium leads to stimulation of chondrocytes to produce inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide and matrix metalloproteases resulting in cartilage damage , .
On the bone level, IL-1 and activation of receptor for nuclear factor B and RANK ligand pathway are key players in osteoclastogensis and the formation of bone erosions. Gouty erosions are characterized by having overhanging edges and partial preservation of joint space. Furthermore, osteoblasts release pro-inflammatory cytokines leading to erosions and bone destruction in addition to compromising their own bone formation function. In the intercritical phase, there is persistent low-grade inflammation in affected joints. The same cytokines responsible for the acute flare up can be found at lower concentrations inbetween attacks. Although chronicity may result even with the use of uric acid lowering drugs and appropriate management of acute flare ups, yet its incidence is lower compared to patients with recurrent inappropriately treated attacks. Chronicity can be decreased by long-term use of low dose anti-inflammatory agents such as colchicine and lowering SUA to safe levels , .
You May Like: Pistachios Nuts And Gout
Does Kidney Disease Cause Your Gout
One of the complications of kidney disease is gout.
A gout is a form of arthritis that is very painful. It is a disorder caused by excess acid in the body.
Gout affects joints. When uric acid exceeds a certain level, it crystallizes and deposited in joints. The crystals are needle-like when viewed under a microscope. Gout primarily affects the big toe.
Uric acid is a result of the breakdown of purines. Some foods such as red meat have more purines than others.
Living With Gout And Kidney Disease
When you have both gout and kidney disease, treating gout can be difficult because some medicines, such as NSAIDs, are not safe for the kidneys. Some of the most common medicines for acute and chronic gout should be adjusted or avoided when you have kidney disease. Learn more about the medicines for gout here.Additionally, some people with kidney disease take medicines that may increase their risk of gout. For example, diuretics and beta-blockers, two common medicines for high blood pressure can contribute to gout attacks. Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take so they can suggest a treatment that works best for you.If you have both gout and kidney disease, there are certain things you can do to keep both conditions under control and improve your general health.
Read Also: Is Pickle Juice Good For Gout
Effects Of Uric Acid From Innate To Adaptive Immune Cells
Uric acid modulates the adaptive immune system via innate immune cells, mostly involving dendritic cells . This feature is well exemplified by the synergistic effect of uric acid on CD8+ T cell priming, during which uric acid induces the expression of costimulatory molecules in dendritic cells. Shi et al. purified low-molecular-weight fractions from ultraviolet-treated 3T3 cells and liver cells by high-performance liquid chromatography and found that these fractions markedly enhanced the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response. The component of the low-molecular-weight fractions not only was degraded by uricase but also exhibited a mass spectrum that matched that of uric acid. Furthermore, the investigators found that uric acid stimulated dendritic cells and macrophages to express the costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86, thereby enhancing the CD8+ T cell immune response.
Clinical Trials Of Uric Acid In Chronic Kidney Disease
Experimental trials of uric acid lowering drugs in CKD have been mixed . One analysis suggested that a primary reason for the mixed results was that some trials were too short or underpowered to show meaningful progression in the control groups, thus making it difficult to show a benefit in the treatment group. In essence, if the control group does not demonstrate worsening of the underlying disease, it is challenging for any treatment to demonstrate protection. Indeed, studies showing meaningful progression :261-2. decrease in the control group over the time course of the study) were associated with a benefit of urate-lowering therapy. This analysis argued for urate-lowering therapy in participants with hyperuricemia and CKD5858 Sato Y, Feig DI, Stack AG, Kang DH, Lanaspa MA, Ejaz AA, et al. The case for uric acid-lowering treatment in patients with hyperuricaemia and CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019 Dec 15:767-75..
Also Check: Onion And Gout
Epidemiology Of The Association
Some genetic studies also suggest that hyperuricemia may confer risk for CKD, especially in Mexican American, Native American, and Italian populations2020 Macias-Kauffer LR, Villamil-Ramirez H, Leon-Mimila P, Jacobo-Albavera L, Posadas-Romero C, Posadas-Sanchez R, et al. Genetic contributors to serum uric acid levels in Mexicans and their effect on premature coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol. 2019 Mar 279:168-73.,3636 Testa A, Mallamaci F, Spoto B, Pisano A, Sanguedolce MC, Tripepi G, et al. Association of a polymorphism in a gene encoding a urate transporter with CKD progression. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Jun 9:1059-65.,3737 Voruganti VS, Franceschini N, Haack K, Laston S, MacCluer JW, Umans JG, et al. Replication of the effect of SLC2A9 genetic variation on serum uric acid levels in American Indians. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014 Jul 22:938-43.. However, a recent large Mendelian randomization study did not find any association between serum uric acid, eGFR, and CKD77 Jordan DM, Choi HK, Verbanck M, Topless R, Won HH, Nadkarni G, et al. No causal effects of serum urate levels on the risk of chronic kidney disease: a Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2019 Jan 16:e1002725..
The Gout And Kidney Disease Connection
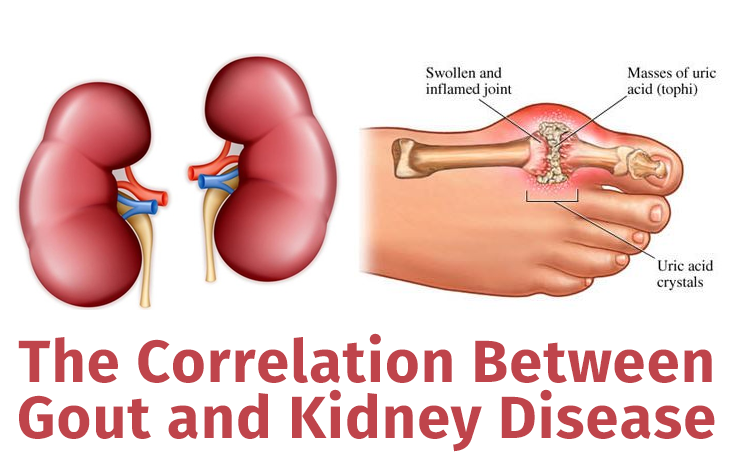
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by too much uric acid. About 1 in 4 people with moderate to severe kidney disease also have gout because diseased kidneys can have a harder time removing uric acid. Even healthy kidneys can only get rid of about 10% of the uric acid they process.
When you have kidney disease, your kidneys dont work as well as they should to remove uric acid from your body. High uric acid levels can cause gout.
When uric acid builds up it can form crystals that damage your kidneys, leading to kidney disease and kidney disease progression.
When you have kidney disease, your kidneys dont work as well as they should to remove uric acid from your body. High uric acid levels can cause gout.
When uric acid builds up it can form crystals that damage your kidneys, leading to kidney disease and kidney disease progression.
Read Also: Onions Bad For Gout
How Can You Prevent Gout If You Have Kidney Disease
- Follow a healthy kidney-friendly diet. Reducing your sodium and protein intake can help you feel your best while maintaining a healthy weight. However, this doesnt mean you need to give up all the foods and drinks you love. Check out these kidney-friendly recipes for inspiration.
- Take your medications as prescribed. Certain medications used to treat gout are not safe for your kidneys. Make sure to talk to your doctor about what medications to take and how frequently.
- Monitor your weight. Obesity is a risk factor for gout. When coupled with kidney disease, it may increase your chances of having gout. Work with your care team to develop a plan for reaching and maintaining a healthy weight. Your care team can also help you monitor your weight and keep track of any changes.
- Maintain a healthy blood pressure. Lowering your blood pressure is important for protecting your kidneys and overall health. Your doctor can help you create a treatment plan to take control of your blood pressure.
- Maintain a healthy blood sugar level. Frequent or ongoing high blood sugar can cause damage to your nerves, blood vessels, and kidneys. To help reduce the risk of an attack of gout, it is important to keep your blood sugar levels balanced.
Gout And Heart Disease
Uric acid is a known risk factor for both hypertension and heart disease. Many epidemiological studies show a link between uric acid and coronary disease, including stroke and heart attack. With higher levels of uric acid in the body, it creates the environment for painful gout flares. And those who have gout are more likely to have heart health issuesincluding heart disease, blocked arteries and heart failure. Left untreated, gout can be very dangerous, with new research showing that having gout doubles a persons risk for heart attack or stroke.
Uric acid is a normal waste product found in your bloodstream.
Having more uric acid than the kidneys can get rid of can lead to a condition called hyperuricemia .
You May Like: Is Onion Good For Gout
Appropriate Dosing Of Xois
As mentioned above, allopurinol dosing in CKD is one of the most controversial areas in gout management owing to the risk of AHS in people with CKD. On the basis of primarily case series and a retrospective casecontrol study, there is general agreement that the starting dose of allopurinol should be low and increased slowly, although no prospective trial data are available to prove or disprove the rationale that such an approach will reduce the risk of AHS. Use of allopurinol is further complicated by the large inter-individual variability in the dose required to achieve the target serum urate concentration . Despite data suggesting that allopurinol dose escalation can achieve target serum urate concentrations even in those with kidney impairment,,, the belief that the allopurinol dose should be reduced in people with CKD remains pervasive. In comparison to allopurinol, febuxostat has a narrower dose range and there has been more willingness to use febuxostat in people with CKD. In the largest study of febuxostat in CKD, which enrolled 96 people with an eGFR in the range 1550ml/min/1.73m2, febuxostat 6080mg daily was associated with a reduction in serum urate concentration with no decline in renal function.
Control Gout And Protect Your Heart Health
Maintaining a healthy serum uric acid level of 6.0 mg/dL or below is important to reduce risk for gout and heart disease. Ask your doctor for a routine serum uric acid blood test to see if you have elevated uric acid. The doctor can also run tests to measure your blood pressure and check your cholesterol levels.
If your uric acid levels are high, your doctor may prescribe medications to keep uric acid levels low and reduce your risk for future gout flares. It is important to take these medications as prescribed and not to stop them without talking with the doctor. It is also important to tell your doctor about all other medications and supplements you are taking, as some may be raising your uric acid levels.
Other stepssuch as drinking plenty of water to flush the kidneys and help to remove uric acid from the bloodstream exercising and maintaining a healthy body weight and avoiding trigger foodsare also important for reducing risk.
To learn more about gout and heart health, . Additional information about heart health is available through the American Heart Association at heart.org.
You May Like: Allopurinol And Alcohol Interaction
How Can I Manage My Gout And Improve My Quality Of Life
Gout affects many aspects of daily living, including work and leisure activities. Fortunately, there are many low-cost self-management strategies that are proven to improve the quality of life of people with gout.
For gout in particular:
- Eat a healthy diet. Avoid foods that may trigger a gout flare, including foods high in purines , and limit alcohol intake .
CDCs Arthritis Program recommends five self-management strategies for managing arthritis and its symptoms. These can help with gout as well.
Uric Acid Production And Handling
Hyperuricemia is a consequence of overproduction or underexcretion of uric acid or a combination of both processes. The content of urate in the human diet is very low. Most uric acid is endogenously generated primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the small intestine. The endogenous production of uric acid is affected by the dietary intake of purine, de novo biosynthesis of purine bases, and degradation and recycling of corresponding nucleotides . Fructose also leads to the generation of uric acid when ATP is consumed during fructose metabolism. Fructose intake has particularly increased in modern society because of the increased consumption of table sugar and high-fructose corn syrup . After its entry into a cell, fructose is converted to fructose-1-phosphate by fructokinase using ATP as the phosphate donor . This process leads to the generation of ADP, which is further degraded into inosine monophosphate, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid. Since these pathways are not regulated by negative feedback, the metabolism of fructose continuously leads to ATP depletion and uric acid accumulation inside cells .
Recommended Reading: Allopurinol Side Effects Alcohol
Medicines For Gout Prevention And Complications
Your doctor can prescribe medicines that can help keep a healthy level of uric acid in your body, which can prevent future gout attacks and the complications from gout. When you have gout, your body either makes too much uric acid, or cannot get rid of enough of it, which causes it to build up. Some medicines are safe to take when you have kidney disease, but some are not. Talk to your doctor about which medicines are safe for you.
Allopurinol
Allopurinol is a medicine for people who make too much uric acid. It is the most common medicine used to treat chronic gout. Your doctor can tell you if allopurinol is safe for you to take if you have kidney disease.
Probenecid
Probenecid is a medicine that works for people who cannot get rid of enough uric acid. It works to remove extra uric acid through your urine. Probenecid can increase your risk of kidney stones. Probenecid is not safe to take for many people with kidney disease, so talk to your doctor for more information about probenecid.
Pegloticase
Pegloticase is an infusion medicine given by injection into your vein at your doctors office, usually every two weeks. It is used for severe chronic gout when other medicines do not work. Pegloticase can quickly bring your uric acid level down to a lower level than most medicines can. Talk to your doctor about whether pegloticase is safe for you.