Get Answers Advice And Medicine
The pain from a gout attack usually gets better in 3 to 10 days. But youâll feel better faster if the gout is treated. If you think you might have it, contact your doctor. An exam and tests will show if itâs gout or something else, like an infection.
Talk with your doctor about the best medicines for you. The type will depend on how well your kidneys work, the possible side effects, and other health issues.
Information About Medicines For Gout
Starting medicines which lower uric acid can set off an attack of gout. You should work with your doctor to learn which medicines and dosages may cause gout flare-ups. In general, it is best to increase the dose slowly over many weeks. Also, you may need a medicine such as colchicine to prevent gout flares for the first several months after starting the urate-lowering medicine. Your uric acid should be lowered to less than 6.0 mg/dL, and sometimes less than 5.0 mg/dL. Gout medications may interact with other drugs. Most people with gout will need to take the urate-lowering medicine for the rest of their life.
Risk Factors For Gout
Gout is more likely to occur in:
- Men. Men have a seven to nine times higher risk of gout than women, although the risk increases for women after menopause
- People with a diet high in purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats , seafood . Processed foods , refined carbohydrates and beverages high in fructose or sucrose also contribute to gout
- Certain ethnicities
- People who overindulge in alcohol, particularly beer and spirits
- People with certain medical conditions , and with some medications or treatments .
Read Also: Almond Milk And Gout
Role Of The Pharmacist
Pharmacists play an integral role in patient education andimproving the care of patients with gout. They can help patientsimprove adherence to pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies.Pharmacists should emphasize lifestyle modifications and diet such asmanaging weight, limiting meat and seafood intake, and minimizingalcohol intake. Pharmacists should also educate patients about theirgout medications, including appropriate dosing, duration of therapy,adverse effects, contraindications, and drug interactions.
Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Inhibitor
Ulodesine
Ulodesine is a novel and unique agent in its class which acts by inhibiting purine nucleoside phosphorylase , an enzyme which is one step before XO in the production of urate . Ulodesine administration has shown a dose-dependent effect on the reduction of xanthine and hypoxanthine . Urate production is inhibited in this way, therefore representing an exciting agent for the management of hyperuricemia in gout. An initial randomized placebo-controlled trial compared oral doses of 40, 80, 120 mg daily in 60 gout patients with a baseline SU over 8 mg/dl . SU was reduced by 2.7, 3.3 and 4.4 mg/dl in the 40, 80 and 120 mg groups, respectively. No placebo-treated subjects achieved the SU goal of less than 6 mg/dl, compared to 33%, 36% and 31% of the subjects receiving the 40, 80 and 120 mg daily doses by the end of 3 weeks. A higher proportion of patients in each respective dose achieved the goal SU at least once during the whole 3 week period. All lymphocyte subsets were decreased by 30â70% with all ulodesine doses, however none of the subjects had to stop treatment due to lymphocyte reduction. No other significant AEs were reported.
You May Like: Allopurinol Side Effects Alcohol
Who Should Diagnose And Treat Gout
The disease should be diagnosed and treated by a doctor or a team of doctors who specialize in care of gout patients. This is important because the signs and symptoms of gout are not specific and can look like signs and symptoms of other inflammatory diseases. Doctors who specialize in gout and other forms of arthritis are called rheumatologists. To find a provider near you, visit the database of rheumatologistsexternal icon on the American College of Rheumatology website. Once a rheumatologist has diagnosed and effectively treated your gout, a primary care provider can usually track your condition and help you manage your gout.
Cautions With Other Medicines
Some medicines and allopurinol can interfere with each other and increase the chances of you having side effects.
Tell a doctor or pharmacist if you’re taking any of these medicines before you start taking allopurinol:
- aspirin or medicines used to thin your blood , such as warfarin
- any antibiotics
- medicines used to reduce your immune response
- tablets that make you pee more such as furosemide or ACE inhibitors to treat high blood pressure such as enalapril and ramipril
If you take aluminium hydroxide , leave a 3 hour gap between the aluminium hydroxide and your allopurinol dose.
Also Check: How Many Cherries Should I Eat For Gout
How To Use Allopurinol
Take this medication by mouth, usually once daily or as directed by your doctor. Take this medication after a meal to reduce stomach upset. If your dose is more than 300 milligrams a day, you will need to take several smaller doses during the day to get this amount .
It is best to drink a full glass of water with each dose and at least 8 more glasses of fluid a day. If your doctor has directed you to drink less fluid for other medical reasons, consult your doctor for further instructions. Your doctor may also instruct you on how to decrease acid in your urine +oral/details” rel=”nofollow”> ascorbic acid/vitamin C).
Dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Use this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same time each day.
For the treatment of gout, it may take up to several weeks for this medicine to have an effect. You may have more gout attacks for several months after starting this medicine while the body removes extra uric acid. Allopurinol is not a pain reliever. To relieve pain from gout, continue to take your prescribed medicines for gout attacks as directed by your doctor.
Tell your doctor if your condition persists or worsens.
Target Audience And Goal Statement
This article is intended for primary care clinicians,pharmacists, rheumatologists, and other specialists who care for patients with hyperuricemia and gout.
The goal of this activity is to provide medical news to primary care clinicians and other healthcare professionals in order to enhance patient care.
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:
You May Like: Is Pistachio Bad For Gout
Taking Allopurinol With Painkillers
You can take allopurinol with paracetamol and anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or indomethacin.
Your doctor may prescribe a NSAID (such as diclofenac or naproxen or a medicine called colchicine to help prevent or to deal with attacks of gout especially in the early stages of allopurinol treatment.
Hyperuricemia And Gout Connection
The explanation of why this happens is obvious. Hyperuricemia literally causes your body to produce and to manage more uric acid that normally which results in urate crystals depositing in joints. Gout is mostly present in toe, elbows, ankles, feet, and knees.
Just because you suffer from hyperuricemia doesnt mean that you will suffer from gout. The risk is increased but the odds are relatively minor. As I have mentioned, only a small percentage develops gout.
Recommended Reading: Are Almonds High In Purines
How And When To Take It
The usual dose of allopurinol is 100mg to 300mg a day. Follow your doctor’s advice on how many tablets to take, and how many times a day.
You’ll have regular blood tests to monitor your uric acid levels. If your uric acid level does not come down far enough, your doctor may increase your dose .
If you have kidney or liver disease, your doctor may prescribe a lower dose and will monitor you more closely.
Uricase Therapy: An Experimental ‘biologic’ Option For Serum Urate Lowering
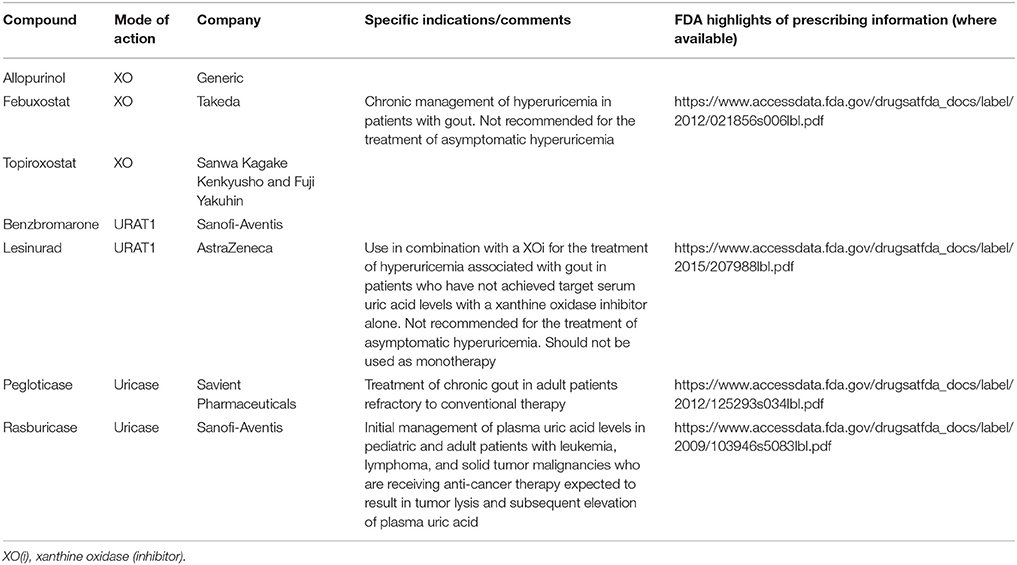
Uricases oxidatively degrade uric acid, thereby catalyzing conversion to soluble allantoin, which is much more soluble than uric acid . Uricases also generate 1 mole of the oxidant hydrogen peroxide for each mole of uric acid degraded .4). Uricase expression was lost in humans and higher primates during the course of evolution . Illustrating the huge role uricase plays in uric acid homeostasis in mammals, normal serum urate in rodents is approximately 1 mg/dL, whereas it is approximately 10 mg/dL in uricase knockout mice. Moreover, untreated hyperuricemia in uricase knockout mice leads to death by renal failure due to severe uric acid urolithiasis.
Enzymatic activity of uricase . Uricase oxidizes uric acid, which is sparingly soluble, to the highly soluble end product allantoin, which is readily excreted in the urine. In doing so, uricase generates not only intermediate forms of uric acid that are subject to further metabolism , but also the oxidant hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct of the enzymatic reaction. During evolution, humans and higher primates lost expression of not only uricase, but also enzymes that rapidly degrade intermediate forms of uric acid generated by uric acid oxidation.
Don’t Miss: Cherry Juice For Gout Mayo Clinic
How Is Pseudogout Treated
There is no cure for removing the calcium deposits that cause pseudogout. It is a progressive disorder that can eventually destroy joints. Treatments for acute attacks of pseudogout are similar to those for gout and are aimed at relieving the pain and inflammation and reducing the frequency of attacks.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are effective for treating inflammation and pain from pseudogout.
- For acute attacks in large joints, fluid aspiration alone or with corticosteroids may help.
- Colchicine may be used for acute attacks.
- Magnesium carbonate may help dissolve crystals, but existing hard deposits may remain.
- Surgery may be required for joint replacement.
Pharmacologic Management Of Gout
Manouchkathe Cassagnol, PharmD, BCPS, CGPAssistant Clinical Professor
Maha Saad, PharmD, BCPS, CGPAssistant Clinical ProfessorQueens, New York
US Pharm
ABSTRACT:Gout is a rheumatic disease thatresults from an excess body burden of uric acid, or hyperuricemia, whichcommonly manifests as recurrent episodes of acute joint pain andinflammation secondary to the deposition of monosodium urate crystals,or tophi, in the synovial fluid and lining. Hyperuricemia is caused byan increased production or a decreased excretion of uric acid, or both.Treatment of gout involves managing hyperuricemia with urate-loweringtherapy and of acute goutyarthritis with colchicine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and/orcorticosteroids. Pharmacists play an integral role in patient educationand improving the care of patients with gout.
Gout is the most common rheumatic disease of adulthood,with a self-reported prevalence of more than 8 million cases in theUnited States, affecting 3.9% of adults, with a male-to-female ratio of3:1.5 However, at an older age the incidence of gout in women approaches the incidence in men.6
New gout guidelines from the American College ofRheumatology have been recently published focusing on the use ofurate-lowering therapy , analgesic and anti-inflammatorymedications for the management of acute gouty arthritis, and drugprophylaxis of acute attacks .1,7
Recommended Reading: Is Rice Good For Gout
Preventing An Attack During Travel
Travel may increase the risk for gout attacks. Travel not only increases stress but eating and drinking patterns may change. Before traveling, patients should discuss preventive measures with their health care provider. The doctor may prescribe taking a corticosteroid at the first sign of a gout attack. In most cases, this stops the attack.
How Hyperuricemia And Gout Develop
Metabolism of Purines
The process leading to hyperuricemia and gout begins with the metabolism, or breakdown, of purines. Purines are compounds that are important for energy. They are part of the nucleic acids that are present in all cells of the body. Purines can be divided into two types:
- Endogenous purines are produced within human cells.
- Exogenous purines are obtained from food.
The process of breaking down purines results in the formation of uric acid in the body. Most mammals, except humans, have an enzyme called uricase. Uricase breaks down uric acid so it can be easily removed from the body. Because humans lack uricase, uric acid is not easily removed and can build up in body tissues.
Uric Acid and Hyperuricemia
Purines in the liver are converted to uric acid. The uric acid enters the bloodstream. Most of the uric acid goes through the kidneys and is excreted in urine. The remaining uric acid travels through the intestines where bacteria help break it down.
The enzyme responsible for production of uric acid from purines is xanthine oxidase. This enzyme is the target of urate-lowering treatments such as allopurinol.
Normally these processes keep the level of uric acid in the blood below 6.8 mg/dL. But sometimes the body produces too much uric acid or removes too little. In either case, the level of uric acid increases in the blood. This condition is known as hyperuricemia.
You May Like: Gout And Almonds
Why Is This Medication Prescribed
Allopurinol is used to treat gout, high levels of uric acid in the body caused by certain cancer medications, and kidney stones. Allopurinol is in a class of medications called xanthine oxidase inhibitors. It works by reducing the production of uric acid in the body. High levels of uric acid may cause gout attacks or kidney stones. Allopurinol is used to prevent gout attacks, not to treat them once they occur.
Challenges In Translating Novel Gout And Hyperuricemia Therapies To Better Clinical Practice
Compliance of gout patients with therapy appears lower than that for therapy of a variety of other common medical conditions, including hypertension, diabetes, osteoporosis, and hyperlipidemia . Younger gout patients with fewer co-morbidities and fewer office visits are the least compliant gout patients, and we need to address systematic failures in both physician and patient education in gout treatment. Physicians appear to underestimate the impact of gout on quality of life and physical function . Gout patients have more co-morbidities, poorer quality of life and physical function, increased health care costs, and increased adverse cardiovascular outcomes than controls .
Not only patient education, but also quality of care in gout treatment have significant room for improvement . The identification of certain improved outcomes with sustained serum urate lowering below 6 mg/dL has ushered in a new era of gout therapy, where practitioners ‘treat to target’ in lowering serum urate . Now the true definition of ‘treatment-refractory’ gout and gout-specific quality of life and disability will need careful assessment and direct attention in clinical practice. Such efforts would be timely, since ‘treatment-refractory’ gout, associated with an overall decrease in quality of life , has been proposed as a specific indication for aggressive urate-lowering strategies and possibly for initially lower serum urate targets than the widely used metric of < 6 mg/dL .
Also Check: Black Cherry Juice For Gout Cvs
What Increases Your Chances For Gout
The following make it more likely that you will develop hyperuricemia, which causes gout:
- Being male
Gout Therapy: How The Current Armamentarium Is Actually Employed In The ‘real World’
Table Table22 summarizes recent assessment of the scope of application of existing therapies for gout in the USA , and also highlights that primary care practitioners are, by far, prescribing the most gout therapies. Given that there are currently estimated to be at least approximately 3 million people with active gout, and 3 to 6 million subjects with a history of gout in the USA , the numbers summarized in Table Table11 suggest that many gout patients receive inadequate therapy. In this context, there appears to be a shortfall in meeting practice guidelines for prescribing of prophylactic colchicine relative to the allopurinol prescription numbers. Overall, the estimated colchicine utilization rate was only 4.6% in office visits for those with gout, versus 8.9% for prednisone and 18% for NSAIDs . As it is elsewhere in the world, allopurinol is the first line choice for serum urate-lowering in the great majority of subjects in the USA. However, there appear to be large differences in prescribing patterns for allopurinol in Caucasians relative to both African-Americans and Asians, suggesting under-treatment of gout in the latter two subgroups.
Don’t Miss: Is Almond Milk Good For Gout
Clinical Diagnosis Of Acute Gout
There is a lack of consensus regarding strict diagnostic criteria for gout in clinical settings.
- A clinical diagnosis of acute gout can be considered in patients who fulfill all of the following parameters:
- Typical clinical presentation
| Diagnostic rule for acute gout | |
|---|---|
| Criterion | |
|
History of previous arthritis attack |
2 |
| Serum uric acid level> 5.88 mg/dL | 3.5 |
|
- Serum uric acid level
- Acute gout flare: often elevated may also be normal or low
- Intercritical stage or chronic gout
- Baseline levels are useful to determine the need for urate-lowering therapy.
- A normal or low level has a very low negative likelihood ratio for a diagnosis of gout.
Serum uric acid levels are not always elevated in acute gouty arthritis.