What Is Gout Its Causes
Gout is actually a type is arthritis that happens due to hyperuricemia, a condition where blood uric acid level increases more the normal level. So, what happens when uric acid increases in our body?
Uric acid present in the blood gets ionized into Monosodium Urate Crystal. Normally these urate crystal gets dissolved and its solubility is affected by:
- Synovial fluid pH,
- Electrolytes level, and
- Other synovial components such as proteoglycans and collagen.
But, when the level of uric acid increases the urate crystal starts deposition gets starts in the tissue around the joints leading to gout. There are two factors that causes the increase in the uric acid level one is overproduction of uric acid and second condition is when there is decreased excretion of uric acid from the body.
Arthritis In The Heel And Ankle
Several types of arthritis, including OA, RA, AS, and PsA, can affect the heels and the ankles.
Symptoms of arthritis in the heel might include:
- Stiffness upon awakening in the morning
- Recurring pain in the heel
- Swelling of the heel
- Limited movement
- Skin changes, including rashes and growths
Inflammation at the heel from RA, AS, or PsA can lead to conditions that cause heel pain. This might include Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, or retrocalcaneal bursitis, a condition in which the bursa becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling.
The ankle is not affected by arthritis as often as other joints, but it can be a source of severe pain and instability when it is affected. Additional symptoms of ankle arthritis include swelling and stiffness of the ankle and problems with mobility. Ankle arthritis will eventually affect gaitthe way a person walks.
Pathogenesis Of Chronic Gout
Chronicity is a feature of gout. It results from chronic inflammation that follows recurrent attacks of gout. Chronic gout manifests by chronic synovitis, bony erosions, cartilage damage and tophi formation. This can be explained by different mechanisms. Presence of urate crystals in the synovium leads to stimulation of chondrocytes to produce inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide and matrix metalloproteases resulting in cartilage damage , .
On the bone level, IL-1 and activation of receptor for nuclear factor B and RANK ligand pathway are key players in osteoclastogensis and the formation of bone erosions. Gouty erosions are characterized by having overhanging edges and partial preservation of joint space. Furthermore, osteoblasts release pro-inflammatory cytokines leading to erosions and bone destruction in addition to compromising their own bone formation function. In the intercritical phase, there is persistent low-grade inflammation in affected joints. The same cytokines responsible for the acute flare up can be found at lower concentrations inbetween attacks. Although chronicity may result even with the use of uric acid lowering drugs and appropriate management of acute flare ups, yet its incidence is lower compared to patients with recurrent inappropriately treated attacks. Chronicity can be decreased by long-term use of low dose anti-inflammatory agents such as colchicine and lowering SUA to safe levels , .
Recommended Reading: Omega 3 Good For Gout
The Four Stages Of Gout
Gout is best understood by seeing it as having four phases or stages :
Stage 1: High uric acid
Elevated uric acid without gout or kidney stone, this stage has no symptoms and is generally not treated.
Stage 2: Acute flares
This stage is marked by acute gout attacks causing pain and inflammation in one or more joints.
Stage 3: Intercritical periods
These are periods of time between acute attacks, during which a person feels normal but is at risk for recurrence of acute attacks.
Stage 4: Advanced gout
This is a stage of chronic gouty arthritis, in which there are lumps of uric acid, or tophi , frequent attacks of acute gout, and often a degree of pain even between attacks .
Figure 1: Stages of Gout
Figure 2: Illustration of Toe Joint with Gouty Tophus. normal toe joint Urate crystals, shown in white, at the “bunion joint,” represent a gouty tophus.)
Figure 3: Progression of Gout
Signs Your Pain Is Likely Gout And Not Something Else
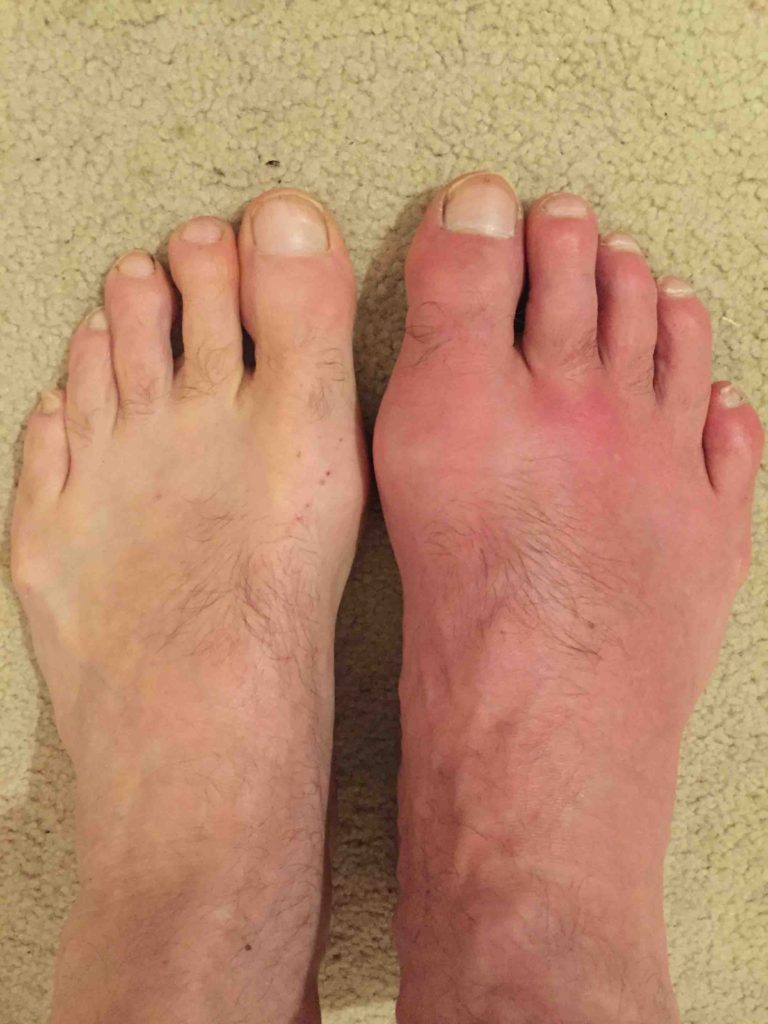
If you develop sharp sudden pain in a single joint or a couple of joints, if the pain is so debilitating that it is hard to walk or wear shoes, and if you have risk factors for gout , theres good reason to suspect gout as the culprit. However, its important to see a doctor for a thorough exam and proper diagnosis.
Dr. FitzGerald cautions that issues unrelated to gout can cause an angry, inflamed joint. Gout may be confused with several other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, including:
- Pseudogout
- An infected joint
- Bacterial skin infection
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
Pseudogout is caused by a different kind of crystal, calcium pyrophosphate. A flare of pseudogout can resemble gout, but it more often affects your wrist and knee, and is unlikely to involve the big toe. Like gout, pseudogout is also considered a form of inflammatory arthritis. Its more likely to affect people over the age of 40 and those who have a thyroid condition, kidney failure, or disorder that affects calcium, phosphate, or iron metabolism, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Its also possible to have gout without the classic presentation of red, hot, sharp, burning, sudden pain in the big toe, foot, ankle, or knee. Some patients may have joint pain that is less acute.
People can also have high levels of uric acid but not develop symptoms of gout.
Recommended Reading: Is Ginger Ale Good For Gout
How Is The Diagnosis Of Gout Made
- Gout is diagnosed in the initial attack by using a needle and syringe to extract a small sample of fluid from around the affected joint space. MSU crystals can be identified under the microscope. This test is also important to rule out other causes of an inflamed joint, such as infection.
- If a biopsy sample is taken, the specimen should be placed in alcohol, as formalin dissolves urate crystals.
- Joint x-rays may show findings consistent with gout, but these findings are not diagnostic on their own. Furthermore, early on in the disease, x-rays may be normal or show soft tissue swelling only.
- Urate levels may be elevated in the blood, but this finding alone is not diagnostic. In some cases, the level may even be below urate saturation.
How Are Gout Attacks Prevented
Maintaining adequate fluid intake helps prevent acute gout attacks and decreases the risk of kidney stone formation in people with gout. Alcohol is known to have diuretic effects that can contribute to dehydration and precipitate acute gout attacks. Alcohol can also affect uric acid metabolism and cause hyperuricemia. It causes gout by slowing down the excretion of uric acid from the kidneys as well as by causing dehydration, which precipitates the crystals in the joints.
Recommended Reading: Does Gout Show Up On Xray
Signs Of Gout Pictures
For the onset of the disease, gout is characterized by an increased content of uric acid, while the symptoms and signs of gout are completely absent. This stage can last for one to two years, after which the patient may have a gout attack.
Most often this occurs at night after prolonged consumption of alcohol and protein foods. From this point on, it can be assumed that a person has a gout disease.
The first signs of gout can be considered pain that is localized in the joints. Most often, develops gout on the legs . In almost half of all patients, gout occurs on the big toe.
Decreased Excretion Of Uric Acid
Two thirds of urate excretion occurs in the kidneys while the rest is excreted through the gastrointestinal tract . Reduced secretory function of the transporter ABCG2 leads to decreased excretion of uric acid through the GIT resulting in rise of serum levels of uric acid and enhanced renal excretion .
Recommended Reading: Make Gout Go Away Fast
Genes Responsible For Uric Acid Regulation
SLC22A12 gene encodes for the transporter URAT1 present on the apical membrane of renal tubules. SLC2A9 is another gene involved in regulation of UA excretion. It encodes for a transporter protein in the membrane of renal tubules. Polymorphism of both genes results in decreased fractional excretion of UA leading to increased SUA levels. ABCG2 is a gene transporter for UA in the proximal tubular cells of the kidney as well as in the GIT. SLC17A1, SLC17A3 genes are important determinants of SUA levels acting as membrane transporters in the kidenys. Other genes involved in determination of SUA levels include SLC22A11, the glucokinase regulatory protein , Carmil , and near PDZ domain containing 1 genes , .
Treating And Preventing Gout Pain
Gout pain is generally treated in two ways:
- Medications to relieve gout attacks in the short-term
- Preventive medications taken regularly to lower uric acid and stop gout attacks from occurring
While inflammation-fighting drugs are used to relieve pain during gout flares, different medicines are used to lower uric acid levels to prevent future attacks. These include:
- Allopurinol
- Probenecid
Another medication called pegloticase may be recommended for people with chronic gout who have not responded to other uric acid-lowering medication.
While many people with gout can be treated by their primary care physician, if gout is not responding to medication or is progressing with worsening or frequent flares or developing tophi gout deposits, then your primary care physician may refer you to see a rheumatologist who specializes in treating diseases that affect joints, muscles, bones and the immune system.
Taking medication to reduce uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout progression is important, Dr. FitzGerald stresses. If you have risk factors for bad gout, such as kidney disease, or are experiencing frequent attacks, early treatment is better.
Also Check: Best Thing To Take For Gout Pain
Diagnostic Evaluation Of Gout In Foot
What goes into a gout diagnosis? These procedures are options:
- Joint aspiration. Fluid is withdrawn from the joint and inspected for crystals and bacteria.
- Blood tests. White blood cell count, ESR , triglycerides, and kidney function may be elevated.
- X-ray. An x-ray of the affected joint is likely to appear normal during an initial acute episode, but in chronic gout, bone erosion and overhanging edges may be seen.
Risk Factors For Gout
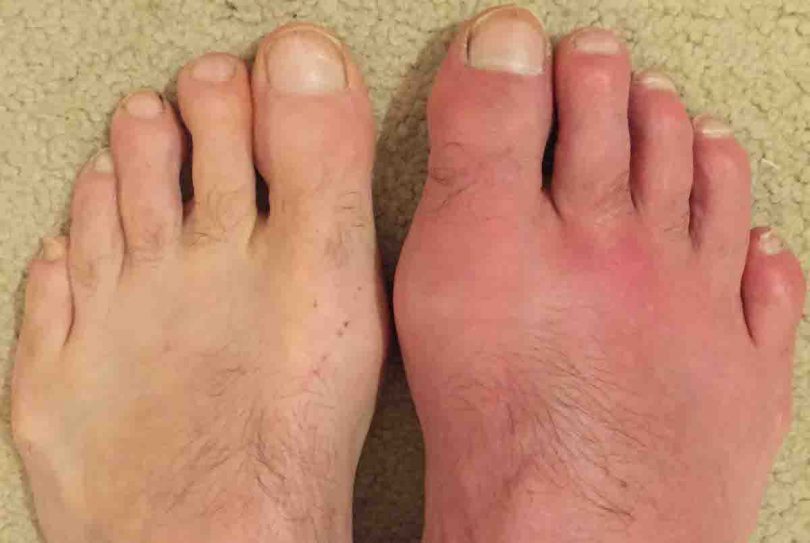
Obesity, excessive weight gain, especially in youth, moderate to heavy alcohol intake, high blood pressure, diabetes, and abnormal kidney function are among the risk factors for developing gout. Certain drugs and diseases can also cause elevated levels of uric acid. Also, there is an increased prevalence of abnormally low thyroid hormone levels in patients with gout.
Recommended Reading: Foods High In Uric Acid Causing Gout
The Pathology Of Gout
Gout is primarily a metabolic disorder in which uric acid accumulates in blood and tissues. When tissue levels reach saturation, needle-like crystals form, causing inflammation. This occurs most commonly in the cooler joints, notably the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
Many people with hyperuricemia never develop gout, but those with the highest levels are most likely to suffer episodes. Hyperuricemia may also lead to kidney stones.
What To Do If You Think You Have Pain Due To Gout
The good news is that there are effective medications to treat gout, Dr. FitzGerald says. In some mild cases, gout can be self-managed with lifestyle changes, such as weight loss if needed and eating fewer high-purine foods .
However, many people with gout should be on a preventive medication to lower uric acid levels and stop flares from occurring. According to the 2020 gout treatment guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology, uric acid-lowering medication is recommended for people who:
- Have two or more gout flares a year
- Have gout tophi
- Have evidence on X-rays of joint damage due to gout
The guidelines, of which Dr. FitzGerald is a coauthor, recommend a treat-to-target strategy, which means treating gout with medication until a target uric acid level is reached.
Unfortunately, gaps in quality care for gout continue to persist and many patients do not take uric acid-lowering medication, which can leave people suffering the intense and persistent pain of gout without relief. This is why it is important to seek medical care if you experience pain that you think could be gout, Dr. FitzGerald stresses.
Gout can be diagnosed several ways, including:
- Removing fluid from the joint to identify urate crystals.
- Using ultrasound to identify several common characteristics of gout, such as collections of crystals in or around joints.
- Using dual-energy CT to detect urate crystal deposits in cases that are more advanced.
You May Like: Does Oatmeal Good For Gout
Causes Of Night Sweats
Night sweat, also known as excessive perspiration or sweating at night, is a very uncomfortable feeling or condition. Even though it is a core part of how the body regulates its temperature and is considered normal, excessive sweating in the middle of the night is another case. Night sweat happens …
What Causes Gout Of The Foot
Gout of the foot is a type of arthritis that often affects the joint at the bottom of the big toe, causing severe pain even when there is no pressure on the foot. This condition is caused when uric acid builds up in the body. If uric acid accumulates in the fluids that surround a joint and forms crystals, the crystals aggravate the joint, causing pain and swelling.
In the past, gout was called the “disease of kings” because it seemed that only royal or noble families were wealthy enough to afford the types foods and amounts of alcohol that were thought to cause it. In fact, during certain time periods, and as recently as the turn of the 20th century, having gout added to a person’s social prestige. Today, while changes in diet may be part of the treatment recommended for gout, medications are also used treat it. In addition, having gout does not have the prestige that it did in the past.
Although the mechanics of how gout of the foot develops are known, the exact causes are less understood. It occurs more commonly in men than in women, although the odds of a woman developing gout increase after she becomes postmenopausal. There is evidence that the condition may have a genetic factor and run in families. Drinking alcohol and taking certain types of water pills may also increase the risks of developing gout.
Read Also: Does Gout Cause Foot Swelling
What Causes Gout Pain
Picture a collection of glass shards pressing outward like needles. This is what it can feel like during a gout flare, when a buildup of uric acid in the blood forms microscopic crystals that grow in and around a joint. As the build-up increases, the immune system responds to these crystals, causing inflammation that leads to visible swelling, redness, and debilitating pain.
In some cases, a gout flare can even lead to a fever and look like an infected joint, Dr. FitzGerald notes. The treating doctor may need to look for possible source of infection, often by removing fluid from the joint to send to the lab to look for crystals or bacteria.
Uric acid is a byproduct of the body breaking down proteins called purines from your own cells and from certain foods such as red meat and shellfish. Alcohol and drinks sweetened with high fructose corn syrup are also high in purines. Normally, uric acid dissolves in your blood and is filtered out through your kidneys, but when your body produces too much uric acid or your kidneys fail to filter it, either due to familial causes or kidney disease, then the uric acid builds up and creates the needle-like urate crystals that cause gout and can also form kidney stones, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Certain factors make some people more likely to develop gout, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gout risk factors include:
How Is Gout Diagnosed
In a clear-cut case, a primary care physician can make the diagnosis of gout with a high level of confidence. However, often there are two or more possible causes for an inflamed toe or other joint, which mimics some of the symptoms of gout, so tests to identify the presence of uric acid is performed.
Since the treatment for gout is lifelong, its very important to make a definitive diagnosis. Ideally, the diagnosis is made by identifying uric acid crystals in joint fluid or in a mass of uric acid . These can be seen by putting a drop of fluid on a slide and examining it using a polarizing microscope, which takes advantage of the way uric acid crystals bend light. A non-rheumatologist, when possible, can remove fluid from the joint by aspirating it with a small needle and send it to a lab for analysis. A rheumatologist is likely to have a polarizing attachment on their microscope at their office. Gout crystals have a needle-like shape, and are either yellow or blue, depending on how they are arranged on the slide .
Figure 11: Uric Acid Crystals Under Polarizing Light Microscopy
There are many circumstances where, however ideal it would be, no fluid or other specimen is available to examine, but a diagnosis of gout needs to be made. A set of criteria has been established to help make the diagnosis of gout in this setting .2
Table 1: Diagnosing gout when no crystal identification is possible
Ideally, 6 of 10 features will be present of the following:
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Gout In Your Big Toe
The First Twinge Of Stiffness Or Dull Ache
Gout ankle starts with a twinge of pain or a dull ache. Then along with the pain, stiffness starts to set in these are the first signs of gout and the alarm to take action. These gout symptoms in the ankle will only quickly get worse if left unattended.
The reason that an attack grows slowly, is because more and more uric acid continues to crystallize. Taking measures to alkalize neutralize the acidity helps to dissolve the crystals that have already formed, but more importantly, helps to keep the uric acid in solution and keep it from crystallizing in the first place.