Is Gout A Risk Factor For Incident Heart Disease
One of the key metabolic abnormalities in gout, hyperuricaemia, is known to be associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, although causality has not been proved. On the other hand, while there are some data suggesting that gout is a risk factor for incident heart disease, the overall literature in the area is somewhat mixed and debateable . The authors also cite it as the main reason for conducting the current study. The risk imparted by hyperuricaemia is of a small magnitude compared to other traditional cardiovascular risk factors, but it is significant. In addition, hyperuricaemia has also been shown to be a risk factor for peripheral vascular disease, another manifestation of atherosclerosis., Some studies indicate that gout is an independent risk factor for incident cardiac disease .
Summary of large studies assessing the risk of cardiac disease in patients with gout
Ua And Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Cardiomyocyte apoptosis is one of the pathogeneses of myocardial anatomical reconstruction. Oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress are the key factors promoting apoptosis, which are involved in the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cardiovascular diseases. UA triggers oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress to signal the network to induce endothelial dysfunction via activating the protein kinase C pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells . The latest research also demonstrates that UA can induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vitro and in vivo, and its molecular mechanism might be through the activation of calpain-1 and the endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway . So far, the studies on UA-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress is scarce, but it is certain that there will be more research to clarify the relationship between the two in the future.
Treating Gout And Diabetes
Patients need to know that both are chronic diseases treatable but not curable so they need to work with their health care providers to ensure they are treating both, says Dr. Bose.
Most patients with gout need to be on a medication that lowers their uric acid levels. And type 2 diabetes management depends on ideal control of body mass through diet and exercise as well as medical management of glucose levels, says Dr. Edgerton.
For gout, that means uric acid-lowering medication like allopurinol or febuxostat. People with type 2 diabetes either take medications to lower their blood sugar levels or to increase insulin production . And its safe to take medications for both conditions, says Dr. Edgerton.
What might get trickier is following exercise and diet recommendations. To improve blood sugar, you need to be more active, but if you have a gout flare or arthritis, that can be tough, says Dr. Edgerton. And a gout-friendly diet doesnt totally overlap with a diabetes-friendly one, he adds.
For example, you might have someone with diabetes being encouraged to kind of do a low-carb or a keto-centric diet. Well, thats not necessarily going to help with the gout, especially if its a high protein diet, which can be more difficult for gout patients.
Read Also: How Many Cherries Should I Eat For Gout
Lodoco2 Trial Presented In A Hot Line Session Today At Esc Congress 2020
Sophia Antipolis, France 31 Aug 2020: Colchicine reduces the risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with chronic coronary disease, according to results of the LoDoCo2 trial presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2020.1
Over a decade, more than one in three heart patients will have another heart attack or stroke, or die from heart disease, despite taking preventive medication, said study author Dr. Mark Nidorf of GenesisCare, Australia. Our study shows that this could be reduced to one in four with the addition of low-dose colchicine.
Colchicine, originally derived from the bulb of the crocus plant, has been used since ancient times to treat inflammation. Now synthetically made, it is a generic medication taken to treat gout. The drug also inhibits several inflammatory pathways known to be important in atherosclerosis. The LoDoCo pilot trial suggested that colchicine 0.5 mg once daily was safe and effective for preventing cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease.
The LoDoCo2 trial randomised 5,552 patients who had chronic coronary disease, and were tolerant to colchicine during a 30-day open-label run-in phase, to colchicine 0.5 mg daily or matching placebo on a background of lipid lowering and antithrombotic therapy.2,3 The primary endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke, or ischaemia-driven coronary revascularisation.
High Levels Of Uric Acid

People with gout tend to have high levels of uric acid . And some large-scale studies, including the Framingham Heart Study, which followed several thousand people over many years, have found that patients with high uric acid levels have a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes as well as metabolic syndrome. This is especially true for women.
But a 2021 study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology didnt find this relationship in fact, researchers speculated that insulin resistance led to high uric acid levels and not the other way around.
Read Also: Is Onion Good For Gout
Results Support Need For Interventions To Reduce The Excess Risk In This Population Researchers Say
Older individuals with gout were at increased risk for incident heart failure, a large population-based cohort study found.
Among participants enrolled in the REasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke study, the multivariate-adjusted hazard ratio for heart failure hospitalization for those with gout was 1.97 compared with patients without gout, according to Lisandro D. Colantonio, MD, PhD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
And gout also was associated with an elevated risk for heart failure hospitalization with both reduced and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction , the researchers reported online in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
Previous research has demonstrated that gout is associated with coronary heart disease and stroke, and the conditions also share many risk factors such as obesity, hypertension, and diabetes — which also have been linked with heart failure.
“If gout is associated with an increased risk for heart failure, this would support the need for interventions to prevent its occurrence in this population,” Colantonio and colleagues wrote.
To explore this, they analyzed data from individuals enrolled in REGARDS from 2003 to 2007 who were 65.5 years of age or older, excluding those with a history of coronary heart disease, heart failure, or stroke.
A limitation of the study, they said, was its reliance on claims data.
Disclosures
Primary Source
Arthritis Research & Therapy
Why Does The Cardiovascular Risk With Gout Differ By Sex
Heart disease risk differs by sex in the general population. Women have a lower risk of heart disease compared to age-matched men in the pre-menopausal yearsa protective effect of oestrogen. This benefit is lost in post-menopausal years and therefore the risk of heart disease in post-menopausal women catches up with men’s risk of heart disease. Despite the differences in prevalence rates, the same risk factors for heart disease are key in both men and womenthat is, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, and family history of heart disease. The early evidence from the current study and some others indicates that the increase of heart disease risk might differ slightly by sex, the association being stronger in women compared to men. The absolute risk of any cardiovascular disease was 24.0/1000 person-years in men and 23.1/1000 person-years in women with gout, compared with 19.2 and 14.8/1000 person-years in men and women without gout, respectively. This shows that there is a difference in the risk of cardiovascular disease by sex in patients without gout and that this sex difference in cardiovascular disease risk is abolished in men and women with gout. It is possible that systemic inflammation induced by gout in women, who otherwise have a lower prevalence of cardiac risk factors than age-matched men, is more atherogenic than that in men. Studies are needed to test whether there are sex-based differences in the pathogenesis of gout-associated heart disease.
Recommended Reading: Allopurinol And Alcohol Interaction
Gout: A New Heart Disease Risk Factor
For the 8 million Americans who suffer from gout, sudden and severe attacks of pain in the joints arent the only things to worry about. A new study in the Annals of Rheumatic Diseases shows that the majority of people presenting with this common form of arthritis are at a very high risk for cardiovascular disease and prevention tactics should be paramount. For Heart Health Month, we examine this connection.
Gout is caused by increased uric acid in the blood, which deposits crystals in the joints, sparking an inflammatory responsethe same process that often leads to dangerous blood clots, triggering heart attacks and strokes.
In the study, from the Hospital General Universitario de Alicante in Spain, researchers examined 247 patients presenting with gout. They evaluated traditional risk factors for heart disease and used common risk prediction tools to stratify the patients according to their cardiovascular risk.
Some 142 patients not initially placed in the very high-risk category based on the standard assessments also had an ultrasound of their carotid arteries. Of these, researchers found, 46 percent had a build-up of fatty plaque. Based on the findings, patients with gout classified as being at very high risk for cardiovascular disease jumped from 40 percent to a whopping 68 percent.
Gout And Heart Disease
Uric acid is a known risk factor for both hypertension and heart disease. Many epidemiological studies show a link between uric acid and coronary disease, including stroke and heart attack. With higher levels of uric acid in the body, it creates the environment for painful gout flares. And those who have gout are more likely to have heart health issuesincluding heart disease, blocked arteries and heart failure. Left untreated, gout can be very dangerous, with new research showing that having gout doubles a persons risk for heart attack or stroke.
Uric acid is a normal waste product found in your bloodstream.
Having more uric acid than the kidneys can get rid of can lead to a condition called hyperuricemia .
Also Check: Are Almonds Good For Gout
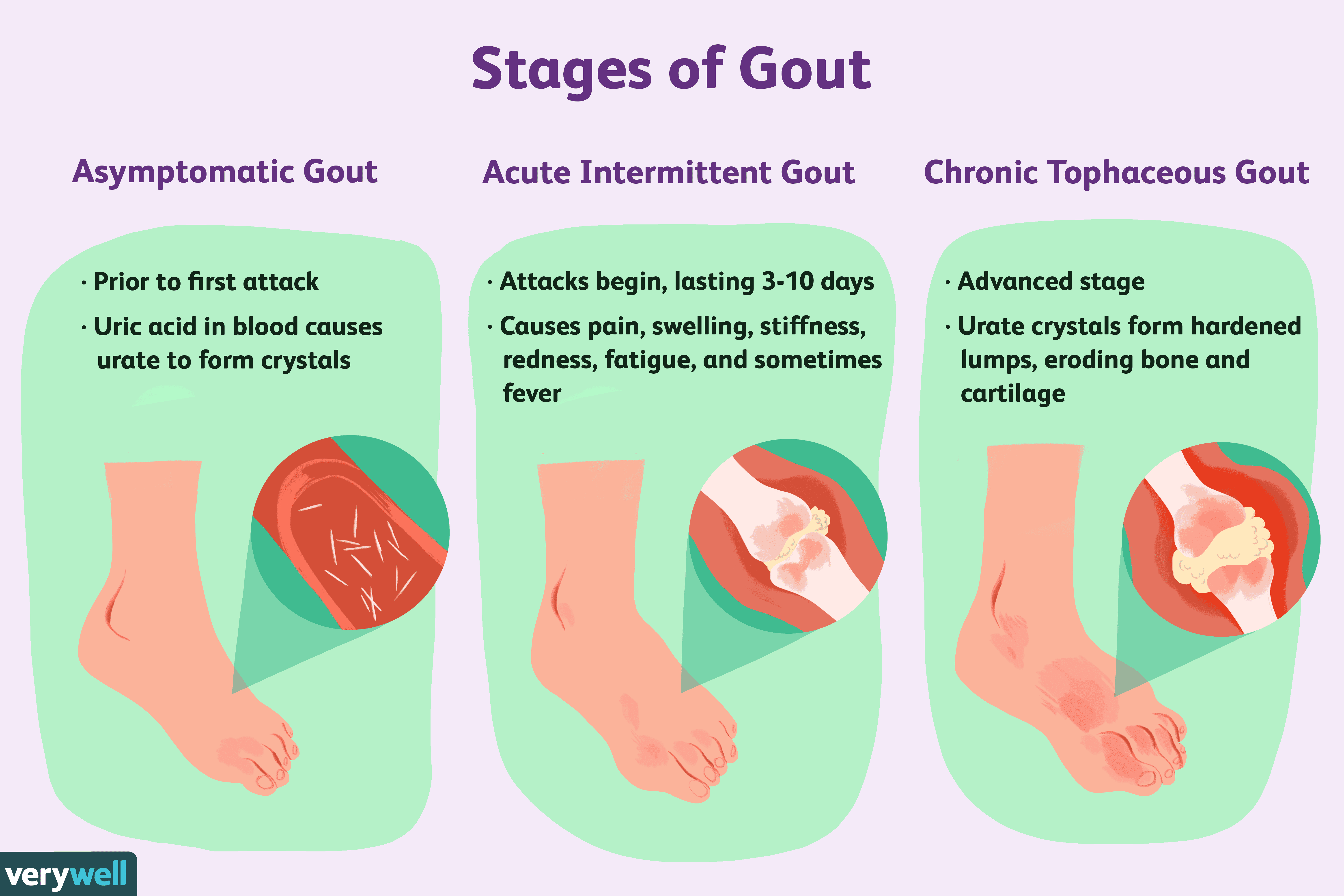
How Can I Manage My Gout And Improve My Quality Of Life
Gout affects many aspects of daily living, including work and leisure activities. Fortunately, there are many low-cost self-management strategies that are proven to improve the quality of life of people with gout.
For gout in particular:
- Eat a healthy diet. Avoid foods that may trigger a gout flare, including foods high in purines , and limit alcohol intake .
CDCs Arthritis Program recommends five self-management strategies for managing arthritis and its symptoms. These can help with gout as well.
A New Case Study In Which A Uric Acid Crystals Settled Into The Heart Muscle Of A Patient With Gout Suggests Yes
Many people who have gout also have cardiovascular disease, but whether gout actually causes heart disease has been unclear. After all, heart disease and gout a chronic form of arthritis in which uric acid crystals deposit in the joints share many common risk factors, including obesity, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
If gout does directly cause heart disease, at least in some patients, the assumption has been that systemic inflammation is to blame. While inflammation throughout the body likely plays a strong role, a new case study suggests that its possible for uric acid crystals to actually deposit themselves in the heart muscle.
The case report, which was published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine, describes a 49-year-old man who stopped taking his gout medications after experiencing gastrointestinal side effects. Several months later, he became short of breath, developed swelling in his legs, and was hospitalized. Doctors determined that uric acid crystals had settled into his heart muscle, causing it to become inflamed and damaging it so that it could not pump efficiently .
Although this is a singular case the authors say that no other cases like it have been reported to their knowledge it highlights a possible connection between gout and heart disease.
Recommended Reading: Almonds Good For Gout
Ua And Insulin Resistance/diabetes
Insulin resistance is closely related to diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, hyperuricemia, and other metabolic disorders. Current studies confirm that oxidative stress and inflammation may be the pathophysiological basis of insulin resistance. Hyperuricemia can promote oxidative stress in many cell lines. The rise of ROS level can induce insulin resistance. Oxidative stress may be the cause of insulin resistancerelated cardiovascular complications because overgenerated ROS and insulin resistance may lead to cardiac dysfunction . Our team’s research shows that high UA can increase ROS production and inhibit insulin-induced glucose uptake in H9c2 and primary cardiomyocytes, and N-acetyl-L-cysteine pretreatment can reverse the inhibitory effect of high UA on glucose uptake . The molecular mechanism may be that high UA increases the phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 and inhibits the phosphorylation of Akt, which was blocked by N-acetyl-L-cysteine . Hence, high UA can induce insulin resistance in cardiomyocytes in vitro and in vivo.
Ua And Oxidative Stress
In recent years, a lot of progress has been made on the relationship between UA and oxidative stress and its molecular mechanism. The physiological concentration of UA decreased oxidative stressinduced malondialdehyde and protein carbonyl contents, promoted superoxide dismutase activity, and inhibited the formation of ROS in chicken embryo cardiomyocytes . The underlying mechanism was the NF-E2-related factor 2 signal pathway . In contrast, treated with a high concentration of UA , the Nrf2 signaling pathway was inhibited, malondialdehyde and protein carbonyl contents were increased, and SOD activity was decreased . Our research team found that high UA inhibited the viability of H9c2 cardiomyocytes and increased the production of ROS . Pretreatment with ROS scavenger and extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitor reversed the decrease of cell viability induced by high UA . Further studies show that high UA-induced ROS may be closely related to ERK/p38 activation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /Akt inhibition . In addition, UA has a neuroprotective effect on dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease mice, which may be related to Nrf2-ARE signal activation, reduction of oxidative damage, and neuroinflammation .
Read Also: Allopurinol Side Effects Alcohol
Treating A Gout Attack
As is true for many painful conditions, the first-line treatment for a gout attack is taking one of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , such as diclofenac, ibuprofen, or indomethacin. For people who can’t take NSAIDs, a drug called colchicine is an alternative. It’s been used for centuries maybe even longer specifically for gout. The trouble with colchicine is its side effects, especially the copious diarrhea. If neither an NSAID nor colchicine is an option, then gout attacks can be treated with an oral corticosteroid, such as prednisone, or with corticosteroid injections into the joints.
Uric Acid And Cardiovascular Disease: An Update From Molecular Mechanism To Clinical Perspective
- Department of Internal Medicine, Xiangan Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Uric acid is the end product of purine nucleotide metabolism in the human body. Hyperuricemia is an abnormally high level of UA in the blood and may result in arthritis and gout. The prevalence of hyperuricemia has been increasing globally. Epidemiological studies have shown that UA levels are positively correlated with cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation , and heart failure . Hyperuricemia promotes the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases by regulating molecular signals, such as inflammatory response, oxidative stress, insulin resistance/diabetes, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and endothelial dysfunction. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms are still unclear. Allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, has been shown to improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients with HF, coronary heart disease , type 2 diabetes , and left ventricular hypertrophy . Whether febuxostat, another XO inhibitor, can improve cardiovascular outcomes as well as allopurinol remains controversial. Furthermore, it is also not clear whether UA-lowering treatment can benefit patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia. In this review, we focus on the latest cellular and molecular findings of cardiovascular disease associated with hyperuricemia and clinical data about the efficacy of ULT in patients with cardiovascular disease.
Also Check: Are Onions High In Purines
Does This Mean Gout Patients Should Be Carefully Screened For Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
Considering the ease of screening for risk factors, the suggestion is to screen gout patients older than 35 years with fasting lipid profile and glycated haemoglobin monitoring, blood pressure measurement and current smoking status, and counsel/discuss with the patient if any risk factors are present. Patients should also be screened at regular intervals if their baseline is not normal and managed aggressively. Regardless of causality, the fact remains that patients with gout have a higher prevalence of numerous comorbidities, each of which can contribute to cardiovascular risk, and therefore require appropriate screening and management, as suggested by previous gout guidelines., Since most gout patients receive care from primary care physicians, rather than rheumatologists, this is relatively easy. The only difference from the general population is an earlier age for screening, given the increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with gout and an increased associated risk. The goals are to prevent the onset of heart disease in patients with gout, and in those with early evidence of heart disease based on the workup with traditional markers and surrogates , institute treatments to improve outcomes.